ALPHV ransomware

Introduction
ALPHV/Blackcat is a ransomware family that uses Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) business model. The ransomware is written in Rust Programming language. It is highly configurable using embedded configurations or provided as command line arguments. The malware family has Windows, Linux and ESXi versions. The malware uses AES or ChaCha20 to encrypt the files and delete the volume shadow copies to decrease the possibility of any data survival. It also kills predefined set of services and Processes related to Anti-malware products, Virtualization software and other business-related and backup software. The following graph represents the attack flow of the ransomware.
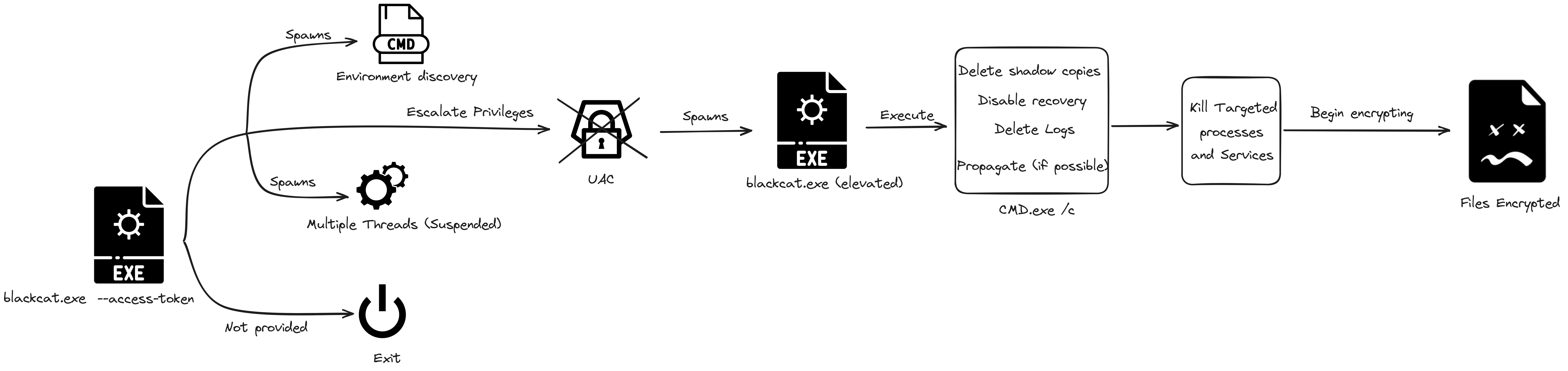
Analysis
Identifying the sample.
The sample was identified by Detect It Easy to be compiled with mingw , this should be some native application. But when I looked at the strings, I knew that it was Rust compiled malware.
Opening the sample in IDA will take some time to do the analysis. Rust binaries are not easy to reverse, especially with stripped -release- binaries. It is statically linked so it is expected to have so many functions and most of them are library and crate functions. Another issue is the strings (all the type system actually), the strings are stored in a structure containing a pointer to the string, length, and capacity.
|
|
The string itself is not null-terminated string so the strings will be mixed. one way to identify the right string is to change the target region to raw data and select the start of the string to the next Xref , this is the termination of the string (Not working all the time).
There are a lot of strange things related to types in rust but will be explained as we move on (if I had to). Another thing to keep in mind is that there will be a lot of function calls related to error checking and memory safety related to Rust so, I will try to avoid wasting too much time to recognize them.
Now we could start, First The main function should be found. The main function will not be clear as in native binaries for example. The start or main function identified by IDA has a lot of unrelated functions to do the initializations and the checks that Rust compiler did (like CRT initializations). The main function is passed to another function, called lang_start .
Originally, the function’s addresses are user_main: 0x0047B1F0 and lang_start: 0x0049BD80. lang_start just call the user main function stored in ecx . user_main also just transfers the execution to sub_48F3C0.
Before going into the assembly to see what this does, I looked at strings for a while and got some interesting findings.
/rustc/532d2b14c05f9bc20b2d27cbb5f4550d28343a36\library\core\src\that string contains the commit hash for the rust version. The rust version used isrustc 1.59.0. it was out in 2021 (nighty version) this could give us a hint about the period of the malware operation.- Configuration of the ransomware.
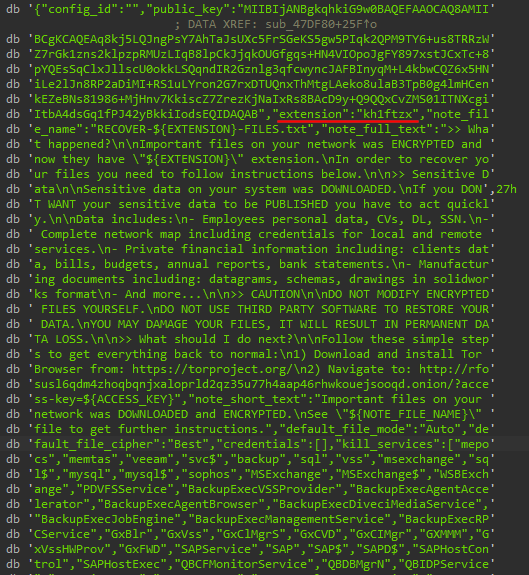
The important thing is the extension: kh1ftzx field. A quick google search reveals the ransomware family is ALPHV/BlackCat Ransomware.
Ransomware running options.
Trying to run the sample.
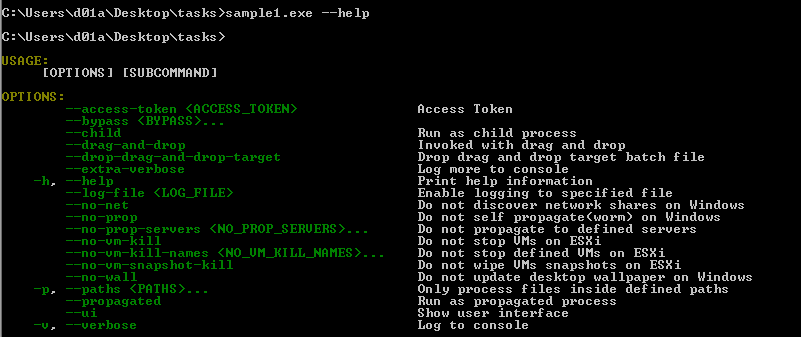
It has a sub-command --access-token which does nothing. Running the sample with any random token will work.
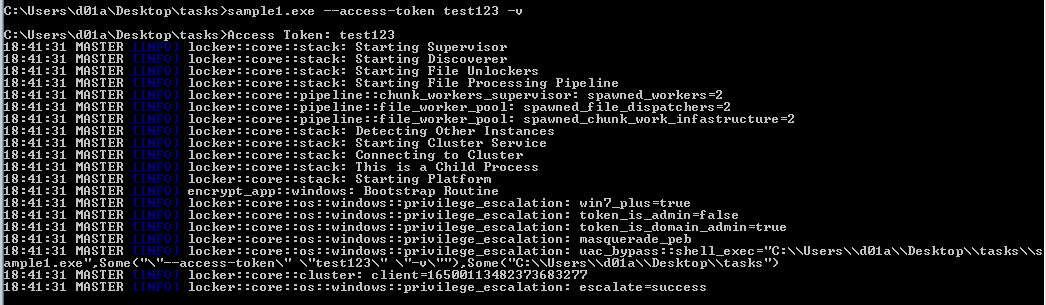
Command Line and Configuration Parsing
Back to user_main , the function calls sub_47DF80 which calls sub_5DFA10. sub_5DFA10 is used to get the Command line used, using GetCommandLineW.
Then it parses the command line string. it extracts the subcommand passed, --access-token was tested and seems like it did nothing with it. Out of this function, back to the previous one sub_47DF80, it continues to parse the Command line checking for -h or --help presence to print the help menu. The help menu is displayed by using the console of the currently running process so in case of using a debugger, AttachConsole argument dwProcessId should be edited to another console process (CMD).
It then loads the hardcoded configurations (Config extractor code at the end of the report) as follows:
|
|
The malware uses open-source library to parse the command line arguments, it is clap crate.
After long time of debugging, the function sub_47DF80 is used to get the command line arguments and extract the configuration passed. And extract the default configurations that hardcoded in the binary.
Debugging issues
The sample broke and didn’t continue in debugger even if the command line edited, but it works in usual CMD. So, to use the debugger we need something to delay execution to attach the debugger in early code. I patched the code and added a call to sleep function followed by INT 3 to instruction (Not shown in screenshot) to make it crash and put a breakpoint in any following instruction and NOP INT3 to continue :).
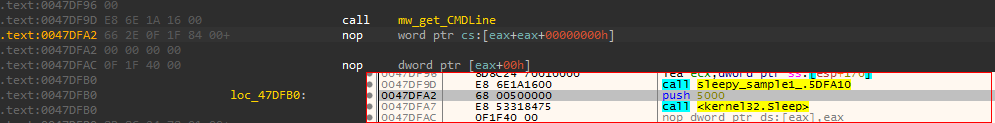
Preparing the environment
The malware retrieves MachineGuid from the registry sub-key SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Cryptography by opening the sub-key and then retrieves the value MachineGuid using RegQueryValueExW
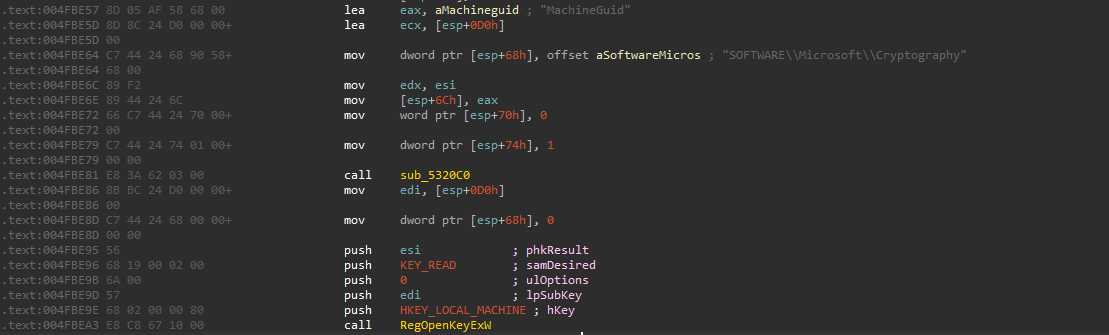
There is no such key in my machine, so it fails to read but anyway it continues.
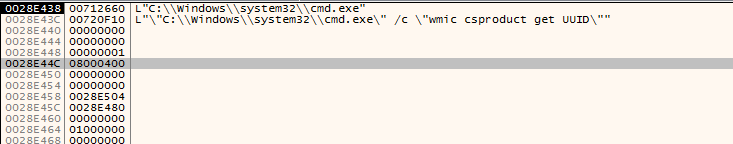
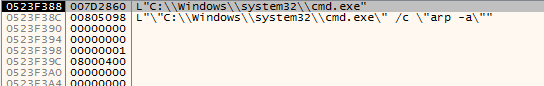
The next step is to execute WMIC command wmic csproduct get UUID But first it should open CMD. It searches for cmd.exe in the current working directory.
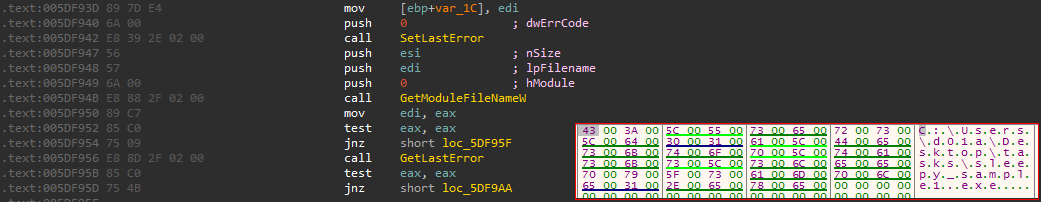
If not found in the current directory, it searches for it in system32
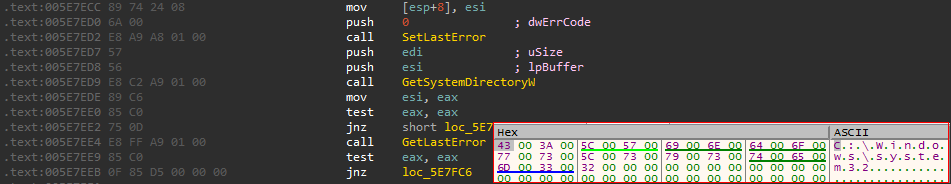
After finding the target executable, the following command is executed. The UUID will be used later to generate access key value to be used to access the malware website on the darknet.
|
|
The malware then Get a handle to a virtual file \\?\nul , I’m not sure but this could be used to redirect any messages to no place.
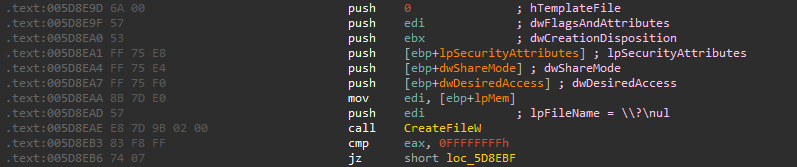
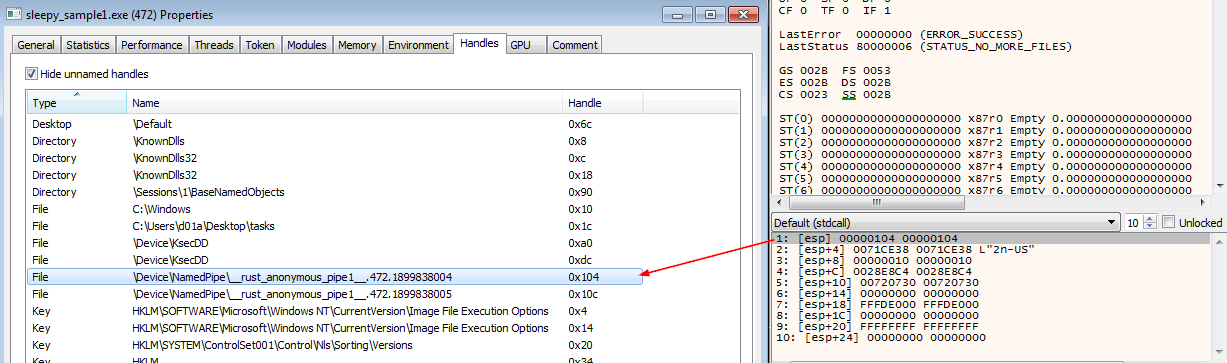
Then, the malware creates a named pipe \\\\.\\pipe\\rust_anonymous_pipe1.<PID>.<RandomValue> to be used in communication in standard OUT (-11)/ERR (-12).
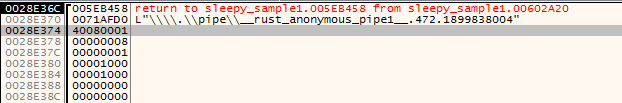
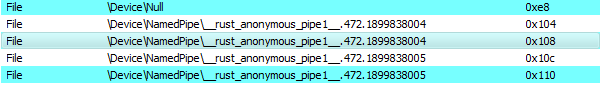
The pipe open mode is PIPE_ACCESS_INBOUND|FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED|FILE_FLAG_FIRST_PIPE_INSTANCE The pipe has access to read, write, and connect operations. and reject remote clients (PIPE_REJECT_REMOTE_CLIENTS). All the handles to the created named pipes.
Finally, it is called CreateProcessW to create CMD process. The created process will be hidden as the flags passed are CREATE_NO_WINDOW|CREATE_PROTECTED_PROCESS.
To receive the return value, WaitForMultipleObjects is used to wait for a previously created events (2 events) then, it reads the output from the previously created pipe.
Gather victim info.
The malware creates some other thread to execute another code section (function at address 0x005EFAA0).
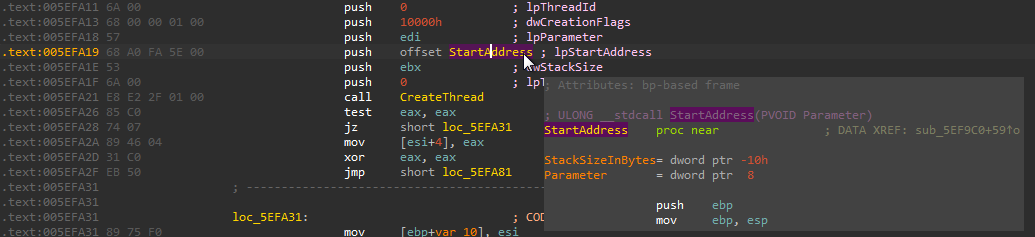
It calls GetSystemInfo to obtain some information about the victim. (_SYSTEM_INFO struct in the memory dump).
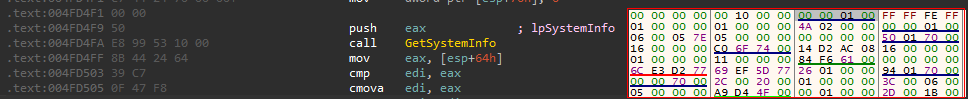
It Also Call ntdll.ZwQueryInformationProcess with ProcessInformationClass=0x0 to get the PEB structure of the currently running process.
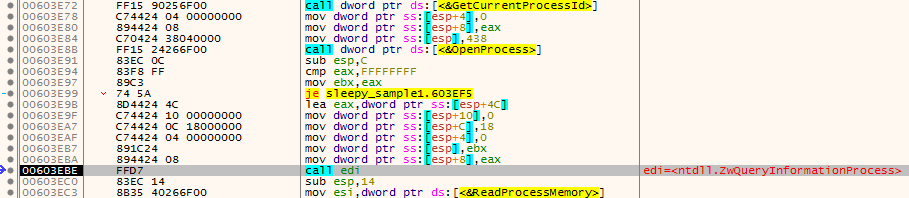
It then calls ReadProcessMemory again to read LDR Structure. Also, it gets uses the same function to get the full path to the currently running executable.
Privilege Escalation (UAC Bypass)
The malware uses COM moniker to bypass UAC and elevate its privileges.
First it calls CoInitializeEx to initialize the COM library.
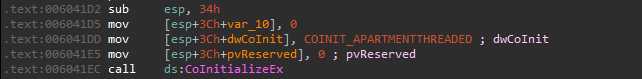
it then uses CLSID = {3E5FC7F9-9A51-4367-9063-A120244FBEC7} which is CMSTPLUA is a COM interface prone to UAC bypass; To call another function that calls CoGetObject .
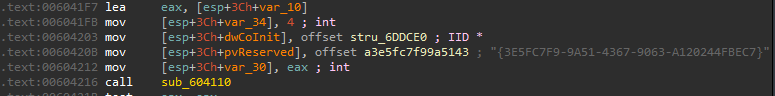
it makes the string Elevation:Administrator!new:{3E5FC7F9-9A51-4367-9063-A120244FBEC7} to elevate the privileges and bypass UAC.

After that, it uninitialized the COM object by calling CoUninitialize ****
According to sophos’ lockbit 3 blog this should left a trace in the registry Key Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ICM\Calibration
the following value.
C:\WINDOWS\SysWOW64\DllHost.exe /Processid:{3E5FC7F9-9A51-4367-9063-A120244FBEC7}
But I couldn’t find it on my machine.
More preparation: elevated Child process to continue
The malware spawns another elevated process that continues execution. After that, it adds a registry key using reg add command. And use the previously mentioned way of executing CMD. The registry key is used to edit the MaxMpxCt member to increase the maximum number of outstanding client requests.
the following command is executed.
|
|
In the same (previous) screenshot we see a usage of fsutil utility in windows that can deal with the windows file system. The commands executed are :
|
|
These commands will be executed to set symbolic links to enable:
- Remote to Remote Symbolic links
- Remote to Local symbolic links
Another command is executed to get the entries of the ARP table.
Then, it tries to reset IIS service by using iisreset.exe /stop .
Delete Shadow Copies
To make sure that all the data are deleted/Encrypted, The malware then deletes all the shadow copies using vssadmin utility. The following are the arguments to CreateProcessW
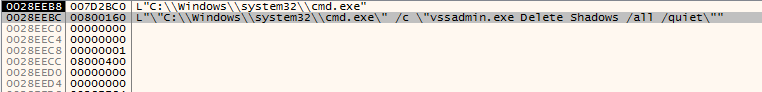
The command executed is:
|
|
Then, it uses wmic utility to delete the shadow copies again.
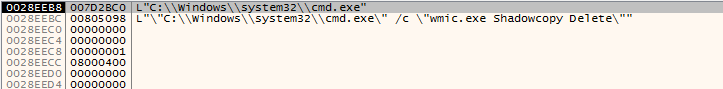
The command executed is:
|
|
Next, it modifies the Bootloader default to disable recovery mode using bcdedit utility. It runs two instances of the command line. The first was not complete so it returns an error message. The second is the following. And it runs successfully:
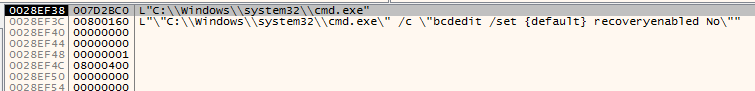
The command executed is:
|
|
Delete Event logs.
Then, it runs the following script:
|
|
This script is used to clear the Event logs entries. It gets all the event logs using wevtutil.exe el and uses wevtutil.exe cl to clear them.
Kill Targeted Services & Processes
Then it is called Global\SvcctrlStartEvent_A3752DX and OpenScManagerW ****according to google, this is used to duplicate windows services. Then it uses EnumServicesStatusExW to list all the services and then kills the services specified in the kill_services in the configurations. For every service, it runs a loop to compare against every entry in the saved kill_services . The targeted services to kill are:
|
|
Same as kill_services , it searches for any running process that included in kill_processes . It gets a list of the currently running processes using CreateToolhelp32Snapshot and iterate through the snapshot using Process32FirstW and Process32NextW
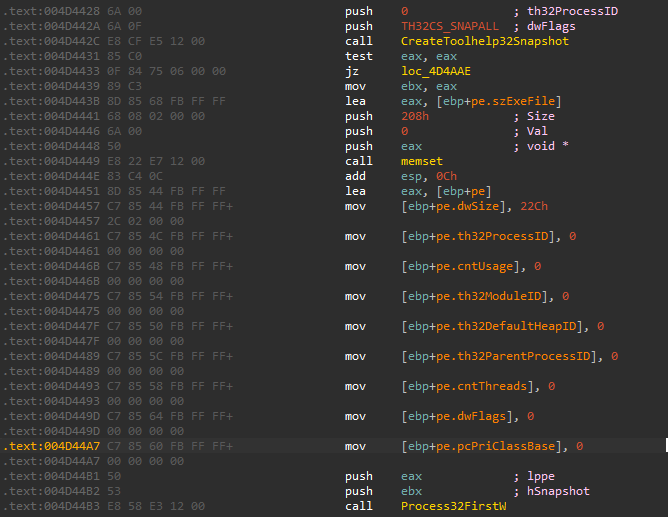
The targeted Processes are:
|
|
The malware lists all the available servers using NetServerEnum to display all the servers on the verbose screen. It Also retrieves the computer name using GetComputerNameW , it will be used in the verbose output.

The next thing it did was to prepare the ransom note file and the image. It dropped on the desktop first before any encryption. Then, while encrypting the files, it will be dropped in every directory.
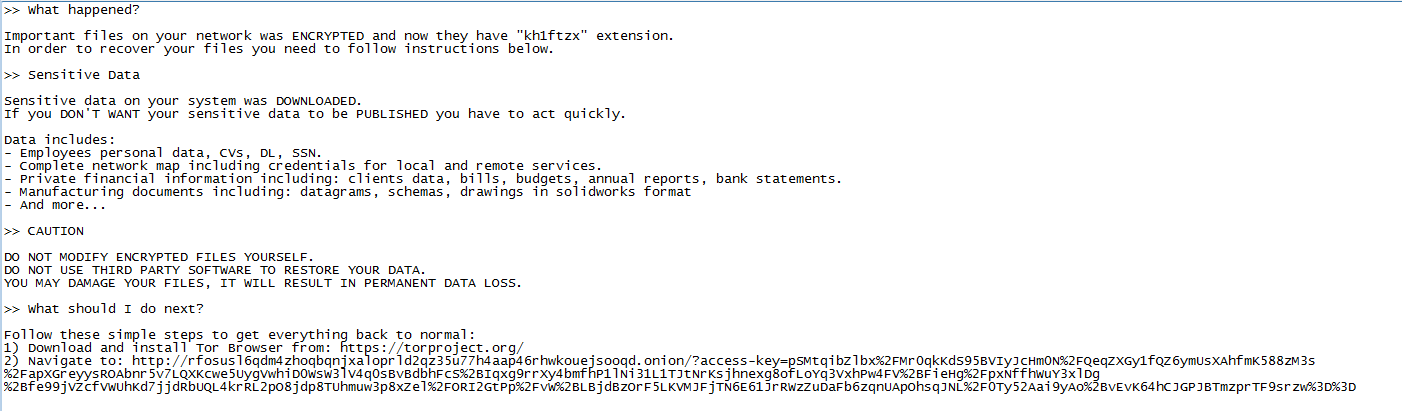
Encryption Mechanism
The malware then looks for a specific locations like previous search queries in C:\Users\<USER>\Searches\Everywhere.search-ms and drops the malware note there too (before encrypting).
it makes three files in the search directory:
- The ransom note.
checkpoints-Everywhere.search-ms.kh1ftzxthat contain a number.Everywhere.search-ms.kh1ftzxthat will be encrypted.
The malware then prepares a configuration data that describes the file being encrypted and it includes encryption mode, the encryption algorithm (chacha20 and AES) and the private key ….
|
|
The Encryption algorithm used is AES. The previous one was for Everywhere.search-ms.kh1ftzx. and the key is randomly generated. The JSON data are used to represent the file and its generated key.
The encryption process starts with adjusting the file pointer to the beginning of the file using SetFilePointerEx

Then, it uses WriteFile to over-write the content. The writing is by appending data (4-bytes then a bigger chunk then the first 4-bytes again) to the end of the file and repeat the process
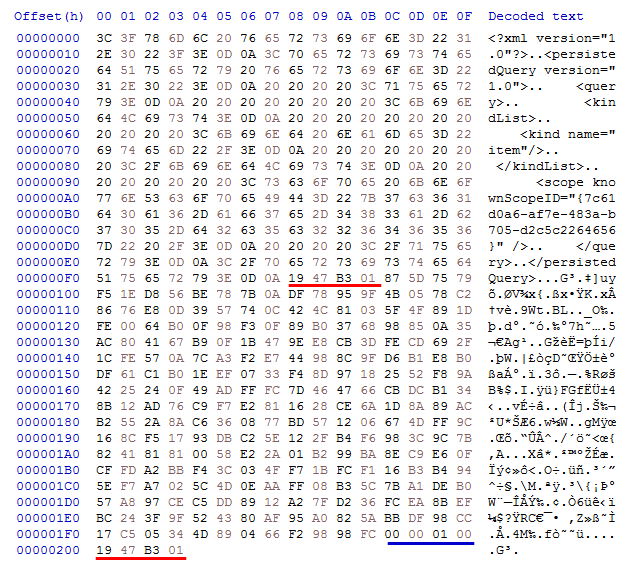
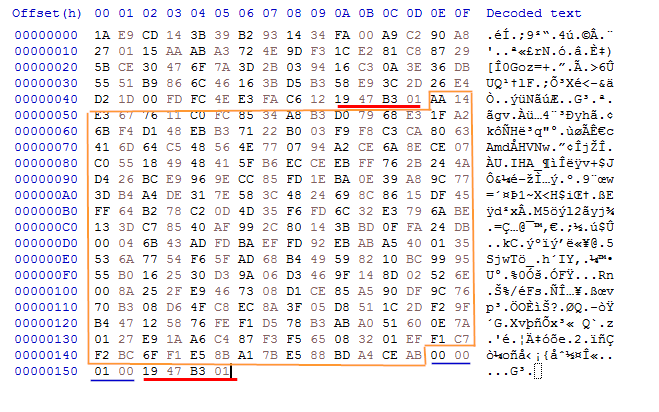
This picture shows the original data (First 0xF8 bytes) delimited by 4-bytes followed by RSA encrypted data (0x100) that contain the JSON data -with AES key- and 4-bytes (00 00 01 00) that was copied before the encrypted text followed by the same 4-bytes delimiter. the first bytes would be then encrypted using AES and the random generated key.
The malware then get a handle to multiple files and read the first 4-bytes of the data. It goes through all the folder under C:\users\<user> and repeat the process. This is done first to the USER directory. Then it uses some Win32 API GetLogicalDrives to get all the available disk drives.
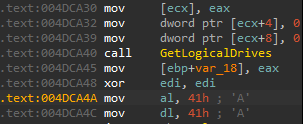
Then, it goes through all the drives using FindFirstVolumeW and FindNextVolumeW . The malware has a list of all the Drive letters. here is a small snippet.
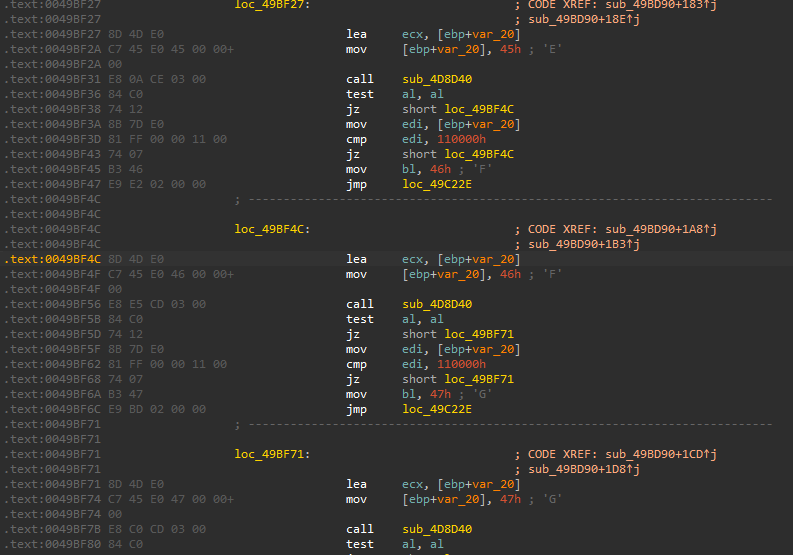
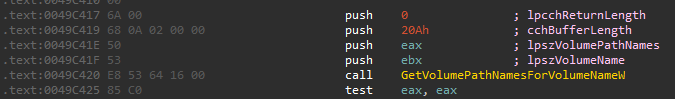
for the found drive, it then uses GetVolumePathNameW to get the path to the mount point of the drive. If there is no path to it, it mount it to the system to encrypt it.
And for every directory, it uses FindFirstFileW and FindNextFileW to get all the files.
The encryption process described for Everywhere.search-ms is applied for all files. It first create a file with the original file name and checkpoint added to the beginning and the ransomware extension. Then, it generates an AES key to be used to encrypt the file and add it to the JSON data. The JSON data is then encrypted using RSA public key provided in the sample data. The RSA encrypted data are delimited by 4-bytes value = 19 47 B3 01. The original file data is then encrypted using AES cipher and the encrypted data is written back.
There are some exclusion paths and file extensions that will not be encrypted. these exclusions are defined in the configurations of the Ransomware.
Example of encrypted file containing the mentioned elements:
The last thing is to drop on the desktop background:
![]()
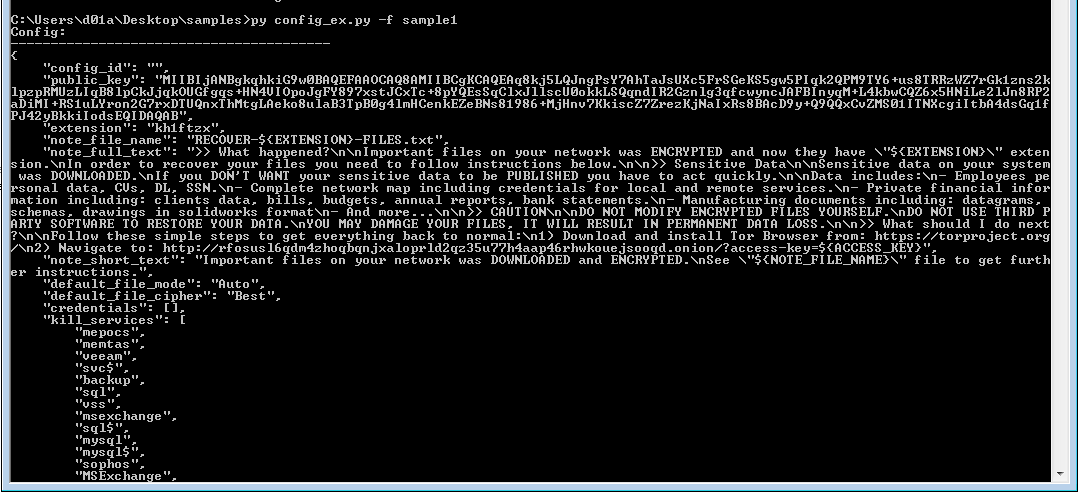
Config Extractor
|
|
Usage:
YARA
|
|
Hybrid-analysis search result Free Automated Malware Analysis Service - powered by Falcon Sandbox - Search results from HA Community Files (hybrid-analysis.com)
IOCs
| IOC | Description |
|---|---|
| ecea6b772742758a2240898ef772ca11aa9d870aec711cffab8994c23044117c | ALPHV sha256 checksum |
| wmic csproduct get UUID | WMIC command |
| vssadmin.exe Delete Shadows /all /quiet | command to delete shadow copies |
| wmic.exe Shadowcopy Delete | command to delete shadow copies |
| bcdedit /set {default} | wrong command used |
| bcdedit /set {default} recoveryenabled No | command to disable recovery |
| cmd.exe /c for /F "tokens=*" %1 in (‘wevtutil.exe el’) DO wevtutil.exe cl "%1" | CMD loop to delete event logs |
| fsutil behavior set SymlinkEvaluation R2R:1 | change filesystem symbolic links |
| fsutil behavior set SymlinkEvaluation R2L:1 | change filesystem symbolic links |
| iisreset.exe /stop | command to reset IIS service |
| arp -a | command to get the ARP table |
| \.\pipe\rust_anonymous_pipe1. |
named piped schema used |
| \?\nul | virtual file used |
| {3E5FC7F9-9A51-4367-9063-A120244FBEC7} | CLSID used to bypass UAC |
| reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters /v MaxMpxCt /d 65535 /t REG_DWORD /f | command to edit lanman server speed |
| SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\MachineGuid | quired registry key |
| checkpoints-<Original_Filename>.kh1ftzx | ransomware-created file |
| RECOVER-kh1ftzx-FILES.txt.png | ransom note wallpaper |
| RECOVER-kh1ftzx-FILES.txt | the ransom notes |
| src/bin/encrypt_app/app.rs | malware source code file name |
| src/core/os/windows/privilege_escalation.rs | malware source code file name |
| src/core/os/windows/samba.rs | malware source code file name |
| src/core/os/windows/system_info.rs | malware source code file name |
| rc/bin/encrypt_app/windows.rs | malware source code file name |
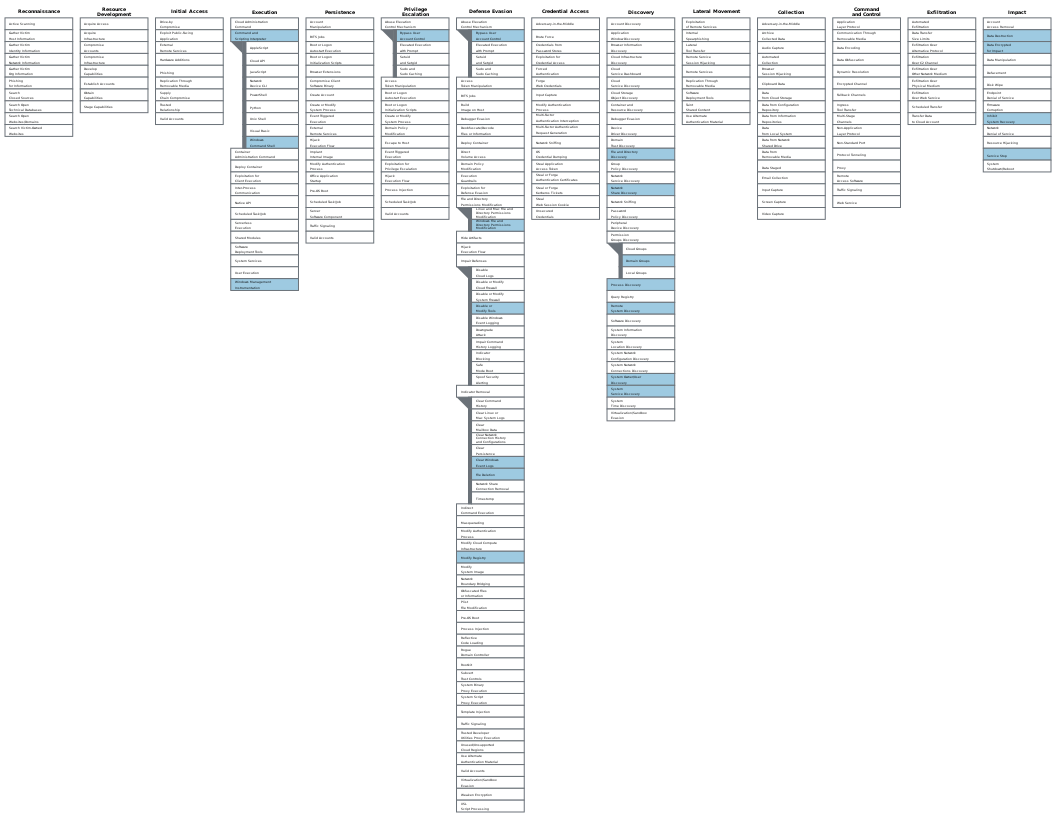
MITRE ATT&CK
References
https://research.checkpoint.com/2023/rust-binary-analysis-feature-by-feature/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q8irLfXwaFM
https://ss64.com/nt/fsutil.html
https://securityscorecard.com/research/deep-dive-into-alphv-blackcat-ransomware/
The many lives of BlackCat ransomware | Microsoft Security Blog